
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
TOPIC: F=ma (Newton’s 2nd law of Motion)
Given the figure below, determine the tension in the three cords (in KN) if the initial pull of the motor is 0.20 m/s, and increased 0.50 m/s each added second.
PLEASE ANSWER WITH COMPLETE AND DETAILED SOLUTIONS. THANK YOU
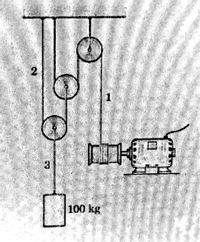
Transcribed Image Text:100 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure shows a person wearing weight boots and doing lower leg flexion/extension exercise in a sitting position to strengthen the quadriceps muscles and a simple mechanical model of his leg. W1 is the weight of the lower leg, W0 is the weight of the boot, the magnitude of the pulling force applied to the tibia by the quadriceps muscles through the FM patellar tendon, the magnitude of the reaction force acting on the FJ tibiofemoral joint. Point O is the center of the tibiofemoral joint, point A is the point where the patellar tendon attaches to the tibia, point B is the center of gravity of the lower leg, point C is the center of gravity of the weight boot. The distances between point O and points A, B and C were measured as a=13 cm, b=27 cm and c=36 cm, respectively. The angle that the long axis of the tibia makes with the horizontal is β=34°, the angle between the line of action of the quadriceps muscle strength and the long axis of the tibia is α=18°. Points O, A, B and C lie…arrow_forward5. The figure below represents the anatomy of the lower limb when balanced on your toes and the body weight acts through the tibia. The Achilles Tendon makes an angle (0) of 8° with the vertical and for this foot x1 is 6.2 cm and x2 is 12.3 cm. Calf Muscle Tibia Achilles Tendon Calculate the tension (T) in the Achilles Tendon if a 70 kg man stands on the toes of both feet. Using the values in this example what is the mechanical advantage for this lever and describe what that means in terms of the efficiency of the lever.arrow_forwardThe figure on the left, below, shows a non-uniform bent rod with a mass of 5 kg. Your job is to determine the location of the center of gravity of this rod. You design an experiment: you connect a pin and cable to the rod such that it safely stays in static equilibrium under a force P that you apply. Then, you apply forces between 0-100 N, and measure the tension force on the cable using a cable tension meter. The results of your experiment are shown in the figure, on the right. Using this experiment, calculate (approximately) the horizontal distance (x in the figure) between point A and the center of gravity G of the bent rod. B C O I 20 cm 20 cm 60° D 50 cm Tension measurement [N] 60 50 40 30 20 -10 0 10 real data estimated fit 20 30 40 ܐܐܝ 50 P[N] 60 70 80 90 100arrow_forward
- Determine the tension developed in the cable AC required to support the traffic light Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ? FAC = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part C Figure 1 of 1 Determine the tension developed in the cable AD required to support the traffic light Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 6 m ? HA 3 m FAD = Value Units 4 m 4 m Submit Request Answer 3 m 4 m 6 m 4 m 3 m y Provide Feedbackarrow_forward1. A weight of 8 lbf is attached to the end of a vertical spring which stretches 4 inches before reaching equilibrium. If the weight is pulled down 6 inches below equilibrium point and given an initial upward velocity of 8 ft/sec, find the equation of motion. Note: In solving for the spring constant k, make sure it ends up as a positive number.arrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY