
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
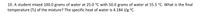
Transcribed Image Text:10. A student mixed 100.0 grams of water at 25.0 °C with 50.0 grams of water at 55.5 °C. What is the final
temperature (Tf) of the mixture? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g °C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A coffee cup calorimeter, including that water it contains, has a heat capacity of 425 J/K, and is initially at a temperature of 23.07 C. A 16.9 gram piece of nickel metal, initially at a temperature of 4.0°C is placed in the calorimeter. The final temperature of the calorimeter and the metal is 22.74°C. What is the specific heat of nickel metal (in Jg1 K-1)? 27 O0.44 1.4 O 25 O 145arrow_forwardThe temperature of a 15-g sample of lead metal increases from 22 °C to 37 °C upon the addition of 29.0 J of heat. The specific heat capacity of the lead is J/g-K.arrow_forward10 A student heats 84.17 mL of water to 95.27°C using a hot plate. The heated water is added to a calorimeter containing 73.92 mL of cold water. The water temperature in the calorimeter rises from 2.15°C to 37.48°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.184 J and the density of water is g. °C 1.00 mL Assuming that heat was transferred from the hot water to the cold water and the calorimeter, determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter. J Heat capacity of calorimeter = °Carrow_forward
- When 6.54 grams of Zn is placed in 500.0 mL of 1.00 M CuSO4(aq) in a coffee cup calorimeter, it reacts completely to displace copper. The temperature of the solution rises from 20.0˚C to 30.4˚C. Assume the coffee cup itself gains no heat and that the solution has the same density (1.00 g/mL) and specific heat (4.184 J/g˚C) as pure water. (a) How much heat does the solution gain during this reaction? (in J)arrow_forwardIron has a specific heat capacity of 0.444J/g-C. 50.0 g of iron at 35C is added to 50.0 g of water with a specific heat capacity of 4.184 J/g-C. When the temperature of the resulting mixture stops changing, the temperature is closer to that of the original water than to the iron. True or false?arrow_forward[11] A 10.00 g sample of a metal alloy was heated to 88.99 °C. It is then quickly dropped into 40.0 g of water in a calorimeter. The water temperature rises from 19.73 °C to 24.23 °C. Calculate the specific heat of the alloy. [Specific Heat of Water = 4.184 J/g °C and Heat Capacity of Calorimeter = 12.6 J/°C]arrow_forward
- A 149.2-g sample of a metal at 74.4°C is added to 149.2 g H20 at 15.5°C. The temperature of the water rises to 18.6°C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of the metal, assuming that all the heat lost by the metal is gained by the water. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J/°C g. Specific heat capacity = | J/°C•&arrow_forwardA 322 gram sample of metal at 78.4°C with a specific heat of 0.138 J/g°C is added to 264 grams of water at 24.2°C. Calculate the final temperature reached the metal-water mixture.arrow_forward4. The heat capacity of copper is 0.382 J/g°.C. A 22.6 g sample of copper at 93° C is placed in 50 g of water at 23.9° C. What is the final temperature of the system?arrow_forward
- When a sample of titanium was supplied 1.00 kJ of energy, the temperature rose 103.5 °C. If the specific heat of titanium is 0.523 J/g · °C, what is the mass of the titanium sample?arrow_forwardA group of students place 15.41g of a metal into a test tube. They place the test tube into a beaker of boiling water until the temperature of the metal was 89.8°C. Then they quickly place the heated metal into a beaker of 10.47g of water with an initial temperature of 16.4°C. The temperature of the mixturecame to rest at 26.1°C. What is the specific heat of the metal used? (CH2O = 4.18 J/g°C)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY