
Examine the network below.
Write the complete LP formulation for this problem. Please include the Objective Function and the complete set of constraints.

Consider the provided diagram,
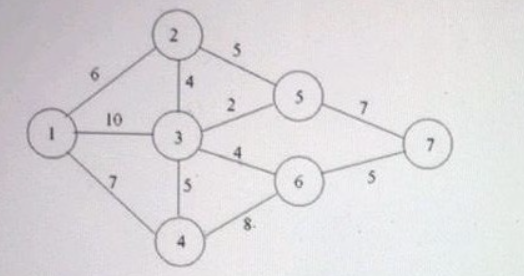
In order to analyze the network given above by linear programming.
let xi (>=0) represent the cost at which we start activity i.
This time is our choice and hence is a decision variable.
- the xi can be constrained to take integer (whole number) values if we so wish using integer programming.
- the xi are NOT necessarily the same as the earliest times.
Considering the precedence relationship between activity 1 and activity 2, it is clear that we must have,
x2⩾
That means, the starting time for activity 2 must be at least as great as the cost for an immediate predecessor activity plus the cost for this predecessor activity. Note that we do not put here. This is because the inequality () gives us more flexibility than the equality (=).
we must also have
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- 8.) A box with a square base and no top must have a surface area of 48 square inches. Find the maximum volume of the box. Make sure to include a labeled picture, and identify any variables and any constraints on the variables.arrow_forwardPart1)An airplane carries water and medical kits to survivors of a natural disaster. The plane can carry a maximum payload of 80,000 pounds. Each container of water weighs 20 pounds, and each medical kit weighs 10 pounds.The cargo space holds a maximum of 6000 cubic feet of cargo. Graph these constraints on the grid provided, and write some units on the axes. Assume each container has a volume of 1 cubic foot. Part2)If each container of water serves 10 people and each medical kit aids 6 people, find the number of water containers and medical kits that could help the most peoplearrow_forwardFind the minimum and maximum values of z = 2x + 3y, if possible, for the following set of constraints. x+y≤9 -x+y≤3 2x-y≤ 12 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. A. The minimum value is B. There is no minimum value. (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. A. The maximum value is B. There is no maximum value. . (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.)arrow_forward
- Type the linear program, optimal solution, and objective function value in a word document. Submit your excel file.arrow_forwardFind the minimum and maximum values of z = 6x + 5y, if possible, for the following set of constraints. x+y≤6 -x+y≤4 2x - y ≤ 10 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. A. The minimum value is B. There is no minimum value. (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. OA. The maximum value is (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) B. There is no maximum value.arrow_forwardFind the minimum and maximum values of z = 3x + 2y, if possible, for the following set of constraints. x+y≤7 -x+y<3 2x-y≤ 10 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. A. The minimum value is. (Round to the nearest tenth as needed.) B. There is no minimum value.arrow_forward
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,






