
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Two 1.5 kg balls are attached to the ends of a thin rod of negligible mass, 72.0 cm in length. The rod is free to rotate in a vertical plane about a horizontal axis through its center. With the rod initially horizontal as shown, a 0.62 kg wad of wet putty drops onto one of the balls with a speed of 3.8 m/sec and sticks to it.
1. During the collision, what is conserved? Linear Momentum,
2. What is the angular speed of the system after the putty wad hits?
3. Through what angle will the system rotate until it momentarily stops?
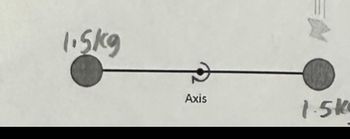
Transcribed Image Text:1.5kg
Axis
*
1.5k
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This time, your mass is 75.2 kg and the sled s mass is 10.5 kg. You re on the sled, initially moving to the west at 6.53 cm/s. From the southern shore, your friend throws a baseball of mass 0.132 kg, which you catch as it s traveling northward with a horizontal velocity component of 28.4 m/s. What will be the sled s (and your) speed after catching the ball? 1 6.28 cm/s 7.85 cm/s 3 4.98 cm/s 4 35.3 cm/sarrow_forwardThis time, your mass is 86.5 kg and the sled s mass is 15.6 kg. You re on the sled, initially moving to the west at 6.31 cm/s. From the southern shore, your friend throws a baseball of mass 0.133 kg, which you catch as it s traveling northward with a horizontal velocity component of 23.1 m/s. What will be the sled s (and your) speed after catching the ball? 6.98 cm/s 3.55 cm/s 19.5 cm/s 2.79 cm/sarrow_forwardA ball of mass 0.34 kg moving with a speed of 2.7 m/s to the right collides head on with a 0.24 kg ball at rest. If the collision is elastic, what is the speed and direction of each ball after collision?arrow_forward
- If a cart of mass 350 grams moving at speed of 4.5 m/s hits an end-stop and rebounds at a speed of 3.2 m/s, what is the change in momentum, in units of kg.m/s? A cart has the rubber bumper attached to the force sensor, and it moves and collides with an end-stop. In the collision, it suffers a change in momentum = 4.05 kg.m/s, and the time during which the collision takes place is 0.182 seconds. Calculate the average force applied on the cart by the bumper, in newtons.arrow_forwardIn an Atwoods Machine lab with m1 = 0.1 and m2 = 0.13 observed acceleration is 1.20 m/s^2. Compare the value with the a(theoretical). During the momentum collision lab a 2.5kg mass moving with 2m/s hits a stationary 5kg mass. After the collision 2.5kg bounces back with 0.5m/s and 5kg mass moves with 1.2 m/s. Calculate Pi and Pf and compare using percent error. Does this experiment show conservation of momentum?arrow_forwardA point particle of mass 3.33 kg is moving with an initial velocity of 2.06 m/s . It collides and sticks to an object of mass 4.58 moving at velocity of -1.67 m/s before collision. What is the speed of the particles after collision? Express your answer in m/s and with two decimal places.arrow_forward
- I need help with question 8?arrow_forwardThe velocity of the center of mass never changes a collision. The final velocity is equal to the initial velocity. 1. A 55 kg skater at rest on a frictionless rink throws a 3 kg ball, giving the ball a velocity of 8 m/s. What is the velocity of the center of mass? 2. A 55 kg skater is skating at 3 m/s to the right with a 3 kg ball in their hands. The skater throws a 3 kg ball, giving the ball a velocity of 8 m/s. What is the velocity of the center of mass?arrow_forwardA 1.99-kg particle has a velocity (2.05 i 2.99 ĵ) m/s, and a 3.01-kg particle has a velocity (1.09 1 + 6.08 j) m/s. (a) Find the velocity of the center of mass. î+ ₁) 1 m/s (b) Find the total momentum of the system. Î+ i) kg. m/sarrow_forward
- A 500-gram ball traveling to the right at 4.0 m/s collides with and bounces off another ball that is initially at rest. The figure shows the momentum vector of the first ball after the collision. Draw (a) the momentum vector of the first ball before the collision and (b) the momentum vector of the second ball after the collision.arrow_forwardThis time, your mass is 90.4 kg and the sled s mass is 21.2 kg. You re on the sled, initially moving to the west at 6.15 cm/s. From the southern shore, your friend throws a baseball of mass 0.124 kg, which you catch as it s traveling northward with a horizontal velocity component of 22.0 m/s. What will be the sled s (and your) speed after catching the ball? 12.8 cm/s 4.63 cm/s 6.61 cm/s 3.01 cm/sarrow_forwardA 1.2 kg ball is kicked at a velocity of 6.97 m/s (E) at a stationary 41.0 kg girl. The ball bounces off her head at a velocity of -1.10 m/s (W). What type of collision is this and what is the velocity of the girl after the collision?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON