
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
No Chatgpt please
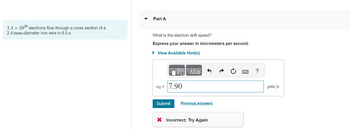
Transcribed Image Text:1.1 × 1020 electrons flow through a cross section of a
2.4-mm-diameter iron wire in 6.0 s.
Part A
What is the electron drift speed?
Express your answer in micrometers per second.
▸ View Available Hint(s)
V
ΕΠΙ ΑΣΦ
V-7.90
Submit
Previous Answers
× Incorrect; Try Again
?
μm/s

Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The quantity of charge q (in coulombs) that has passed through a surface of area 2.00 cm2 varies with time according to the equation q = 4t3 + 5t + 6, where t is in seconds. (a) What is the instantaneous current through the surface at t = 1.00 s? (b) What is the value of the current density?arrow_forwardA high-energy proton accelerator produces a proton beam with a radius of r - 0,90 mm. The beam current is I=9.00A and is constant. The charge density ofthe beam is n = 6.001011 protons per cubic meter, (a)What is the current density of the beam? (b) What is the drift velocity of the beam? (c) How much time does it take for 1.0010 m protons to be emitted by the accelerator?arrow_forwardAn aluminum wire 1.628 mm in diameter (14-gauge) carries a current of 3.00 amps, (a) What is the absolute value of the charge density in the wire? (b) What is the drift velocity of the electrons? (c) What would be the drift velocity if the same gauge copper were used instead of aluminum? The density of copper is 8.96 g/cm3 and thedensity of aluminum is 2.70 g/cm3. The molar mass ofaluminum is 26.98 g/mol and the molar mass of copper is 63.5 g/mol. Assume each atom of metal contributes one free electron.arrow_forward
- What does the term fibrillation mean in connection with heart function? Give two important causes of heart fibrillation in human beings. How do pacemakers and defibrillators help to prolong life for patients suffering from this condition?arrow_forwardA 10.00-meter long wire cable that is made of copper has a resistance of 0.051 ohms, (a) What is the weight if the wire was made of copper? (b) What is the weight of a 10.00-meter-long wire of the same gauge made of aluminum? (c)What is the resistance of the aluminum wire? The density of copper is 8960 kg/m3 and the density of aluminum is 2760 kg/m3.arrow_forwardUnreasonable Results (a) What current is needed to transmit 1.00 102 MW of power at 10.0kV? (b) Find the resistance of 1.00 km of wire that would cause a 0.0100% power loss. (c) What is the diameter of a 1.00-km-long copper wire having this resistance? (d) What is unreasonable about these results? (e) Which assumptions are unreasonable, or which premises are inconsistent?arrow_forward
- A 20.00-V battery is used to supply current to a 10-k resistor. Assume the voltage drop across any wires used for connections is negligible, (a) What is the current through the resistor? (b) What is the power dissipated by the resistor? (c) What is the power input from the battery; assuming all the electrical power is dissipated by the resistor? (d) What happens to the energy dissipated by the resistor?arrow_forward(a) During surgery, a current as small as 20.0A applied directly to the heart may cause ventricular fibrillation. If the resistance of the exposed heart is 300 what is the smallest voltage that poses thisdanger? (b) Does your answer imply that special electrical safetyprecautions are needed?arrow_forwarda) Of what material is a wire made, if it is 25.0 m long with a 0.100 mm diameter and has a resistance of 77.7at 20,0°C ? (b) What is its resistance at 150°C ?arrow_forward
- The quantity of charge through a conductor is modeledas Q=4.00Cs4t41.00Cst+6.00mc .What is the current at time t = 3.00 s?arrow_forwardA close analogy exists between the flow of energy by heat because of a temperature difference (see Section 19.6) and the flow of electric charge because of a potential difference. In a metal, energy dQ and electrical charge dq are both transported by free electrons. Consequently, a good electrical conductor is usually a good thermal conductor as well. Consider a thin conducting slab of thickness dx, area A, and electrical conductivity , with a potential difference dV between opposite faces. (a) Show that the current I = dq/dt is given by the equation on the left: ChargeconductionThermalconductiondqdt=A|dVdx|dQdt=kA|dTdx| In the analogous thermal conduction equation on the right (Eq. 19.17), the rate dQ/dt of energy flow by heat (in SI units of joules per second) is due to a temperature gradient dT/dx in a material of thermal conductivity k. (b) State analogous rules relating the direction of the electric current to the change in potential and relating the direction of energy flow to the change in temperature.arrow_forwardThe current I is measured through a sample of an ohmic material as a voltage V is applied, (a) What is the current when the voltage is doubled to 2V (assume the change in temperature of the material is negligible)? (b) What is the voltage applied is the current measured is 0.27 (assume the change in temperature of the material is negligible)? What will happen to the current if the material if the voltage remains constant, but the temperature of the material increases significantly?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning