
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
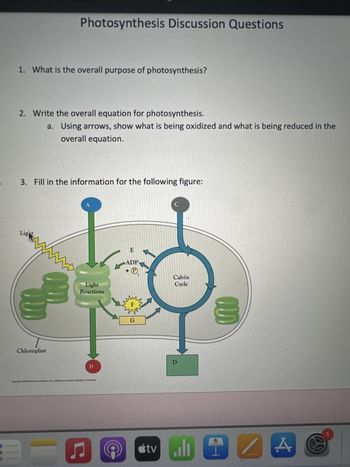
Transcribed Image Text:1. What is the overall purpose of photosynthesis?
2. Write the overall equation for photosynthesis.
a.
Light
Photosynthesis Discussion Questions
3. Fill in the information for the following figure:
Chloroplast
Using arrows, show what is being oxidized and what is being reduced in the
overall equation.
th
Cupright 2008 Pearson Education, ine, publishing as Pea
Light
Reactions
B
Benjamin Cummings
♫
E
ADP
P
Ev
G
C
Calvin
Cycle
D
...
tvill
In

Transcribed Image Text:1. What is the overall purpose of photosynthesis?
2. Write the overall equation for photosynthesis.
a.
Light
Photosynthesis Discussion Questions
3. Fill in the information for the following figure:
Chloroplast
Using arrows, show what is being oxidized and what is being reduced in the
overall equation.
th
Cupright 2008 Pearson Education, ine, publishing as Pea
Light
Reactions
B
Benjamin Cummings
♫
E
ADP
P
Ev
G
C
Calvin
Cycle
D
...
tvill
In
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A. Highlight all the organisms that CAN do photosynthesis (you might need to google search what these are) Venus fly trap Mycorrhizal fungus Cyanobacteria Red algae Sponges Corn (Zea mays) B. Summarize the purpose of photosynthesis______ C. How could you tell or measure the rate of photosynthesis? ____ D. What is a redox reaction? ___ E. When the water molecule donates its electron to the chlorophyll molecule the water molecule was ______ while the chlorophyll was ______. F. When the carbon chain gains electrons from NADPH the carbon chain has been _____. G. Discuss how the chloroplast structure is arranged using the following terms (include picture too) chloroplast, thylakoid, stroma, chlorophyll, H. Light reaction and Calvin cycle: what is the overall purpose of each one?arrow_forwardWrite the overall reaction summary for photosynthesis.arrow_forward34) During photosynthesis, electron transfer follows which sequence? A) sun -> chlorophyll -> electron transport chain -> ATP i vo B) water -> NADPH -> chlorophyll -> electron transport chain -> chlorophyll C) water -> chlorophyll -> electron transport chain -> chlorophyll -> NADPH Jen D) sugar -> electron transport chain -> oxygen -> ATParrow_forward
- 10. Using either the Oxidative Phosphorylation stage of cellular respiration or the Cytochrome complex of photosynthesis, DIAGRAM AND EXPLAIN how electron transport chains function and are used to generate ATP in plants and animals. Make sure to supply sufficient detail to clearly convey your understanding of the process/mechanism.arrow_forwardA mutant form of an Arabidopsis thaliana plant has defective chlorophyll production, such that the abundance of chlorophyll molecules in chloroplasts is 5% the normal level, and the chlorophyll molecules are on average too far apart for resonance energy transfer to occur. What will be the effect on the overall efficiency of photosynthesis in the plant? Rationalize your answerarrow_forward12arrow_forward
- 18. Cyanobacteria, green plants, and green algae generate exactly how many product molecules in their consumption of six CO.molecules and twelve H,O molecules during oxygenic photosynthesis? A. one C,H12O6 molecule, six H,O molecules, and six O, molecules are produced B. twelve C,H1,0, molecules, six H,O molecules, and three CO, molecules are produced C. six H,O molecules and twelve CO, molecules are produced D. six C,H1,0, molecules, three H,O molecules, and six CO, molecules are produced E. twelve H,O molecules and six O, molecules are producedarrow_forward1. During the light dependent reaction, the molecules within the membrane absorb light energy 2. high energy compounds light dependent portion of photosynthesis 3. an electron which is released by a process called and are produced in the in the thylakoid enters where it is energized and used to convert energy. 4. protons travel through located in the thylakoid membrane in a high energy compound. a process known as 5. The three stages of the light independent reaction are to produce and 6. The most abundant protein on earth is 7. You would need molecules of RuBp in order to create 1 molecule of glucosearrow_forward1. Which of the following statements is most accurate? a. The Calvin cycle is a repeating process that uses carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH molecules to allow the cell to produce one glucose molecule. b. Each turn of the Calvin cycle is designed to use a glucose molecule to produce RuBP, 3-PGA, 3-G3P, ATP and NADPH molecules. c. The Calvin cycle is a continuous process that utilizes rubisco molecules to produce RuBP molecules which can be directly converted to glucose molecules for long term energy storage. 2. How many glucose molecules are produced for every turn of the Calvin cycle? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 6 f. 12arrow_forward
- 1. Is carbon dioxide essential for photosynthesis? Justify 2. What is the relationship between photosynthesis efficiency and light intensity? Justify 3. For equal quantities of photons, what is the increasing order of effectiveness (less effective to more effective) of blue, red, green and white light (combination of the three main wavelengths) on photosynthetic activity? Justifyarrow_forward1) What type of organisms can carry out photosynthesis? 2) Why is photosynthesis important? 3) Draw a chloroplast and label the stroma, thylakoid, and granum, and lumen. 4) What is chromatography? 5) Write the equation for photosynthesis: Styles 6) Where do the light and dark reactions or Calvin Cycle occur in the plant? Accessibility: Good to go Q Search L 29 9 darrow_forward4. (4 pts) a) Describe one way in which Rubisco could be improved to optimize photosynthetic activity. b) Why has overexpressing Rubisco not been effective?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education