
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
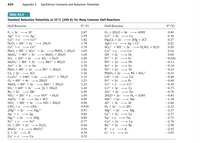
Transcribed Image Text:A24
Appendix 5
Equilibrium Constants and Reduction Potentials
Table A5.5
Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C (298 K) for Many Common Half-Reactions
Half-Reaction
E° (V)
Half-Reaction
E° (V)
F2 + 2e-
Ag2+ + e → Ag*
Соз+ + е —— Со2+
О2 + 2H,0 + 4e
Cu2+ + 2e¯ → Cu
→ 2F-
2.87
> 40H-
0.40
1.99
0.34
Hg2 Cl2 + 2e-
AgCl + e- –→ Ag + Cl-
SO,2- + 4H+ + 2e- → H,SO3 + H2O
Cu2+ + e- – → Cu+
2H+ + 2e
Fe3+ + 3e
1.82
2Hg + 2Cl-
0.27
>
Н,О, + 2H+ + 2е —> 2H,0
Се4+ + e — > Сез+
PbO2 + 4H+ + SO,2- + 2e
MnO4+ + 4H+ + 3e¯ → MnO2 + 2H2O
I04- + 2H+ + 2e
MnO4+ + 8H+ + 5e¯
Au3+ + 3e- → Au
1.78
0.22
1.70
0.20
» PbSO4 + 2H2O
1.69
0.16
1.68
H2
0.00
→ I03¯ + H2O
→ Mn2+ + 4H2O
1.60
Fe
-0.036
1.51
Pb2+ + 2e-
Pb
-0.13
1.50
Sn2+ + 2e-
Sn
-0.14
Ni2+ + 2e
PbO2 + 4H+ + 2e- → Pb²+ + 2H2O
Cl2 + 2e- – → 2Cl-
Cr202- + 14H+ + 6e¯ –→ 2Cr³+ + 7H2O
O2 + 4H+ + 4e-
MnO2 + 4H+ + 2e-
IO3- + 6H+ + 5e-
Br2 + 2e- – → 2B1¯
VO2+ + 2H+ + e¯
AuCl,- + 3e-
NO3- + 4H+ + 3e¯ → NO + 2H2O
CIO, + e- →
2Hg²+ + 2e
Ag+ + e-
Hg22+ + 2e- → 2Hg
Fe3+ + e- –→ Fe2+
1.46
→ Ni
-0.23
PBSO4 + 2e-
Cd2+ + 2e-
→ Pb + SO,²-
→ Cd
→ Fe
1.36
-0.35
1.33
-0.40
Fe2+ + 2e-
2H2O
→ Mn2+
I2 + 3H2O
1.23
-0.44
2H2O
1.21
Cr3+ + e-
Cr2+
-0.50
1.20
Cr3+ + 3e-
→ Cr
-0.73
Zn2+ + 2e
2H2O + 2e
Mn2+ + 2e-
1.09
Zn
-0.76
» VO2+ + H2O
→ Au + 4Cl-
→ H2 + 20H-
Mn
1.00
-0.83
0.99
-1.18
0.96
Al3+ + 3e-
→ Al
-1.66
ClO,-
» Hg,2+
Н, + 2е-
Mg2+ + 2e-
La3+ + 3e-
Na+ + e-
0.954
2H-
-2.23
→ Mg
→ La
0.91
-2.37
→ Ag
0.80
-2.37
0.80
→ Na
-2.71
0.77
Ca2+ + 2e-
> Ca
-2.76
O2 + 2H+ + 2e- → H2O2
MnO4- + e¯ → MnO,2-
I2 + 2e- –
Cut + e - → Cu
0.68
Вa2+ + 2e- — Ва
-2.90
0.56
K+ + e¯ –
→ K
-2.92
→ 21-
0.54
Li+ + e¯ –→ Li
- 3.05
0.52

Transcribed Image Text:1. Use the table of standard reduction potentials on page A24 of your textbook to pick
a reagent that is capable of each of the following reductions (under standard
conditions in acidic solution).
a) Reduces Cu²+ to Cu but does not reduce Cu2+ to Cu+
b) Reduces Br2 to Br- but does not reduce I2 to I-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using data from the Standard Reduction Potentials table, place the following in order of increasing strength as oxidizing agents (all under standard conditions). (Use the appropriate symbol to separate substances in the list.) Cr³+, Ba²+, Au³+, Cu²+, K+, and Cd²+ Help chemPad XX → Greekarrow_forwardUse standard reduction potentials to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: Hg2+(aq) + Ni(s) Hg(1) + Ni2+(aq) Answer: kJ K for this reaction would be v than one. greater lessarrow_forwardUse standard reduction potentials to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: 2Fe*(aq) + Ni(s)- →2FE?*(aq) + Ni²+(aq) 2+ Answer: kJ K for this reaction would be than one.arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction and standard reduction potential data. 2Ag (aq) + Cu(s) 2Ag(s) + Cu*"(aq) Half reaction E°(V) Ag (aq) +eAg(s) 0.80 Cu2"(aq) + 2e → Cu(s) 0.34 a. As written, is the Keg of the reaction shown above greater than 1 or less than 17 (Select] b. Which species is the reducing agent? [Select ] c. Suppose a voltaic cell was constructed using a Cu and Ag electrode (pictured below). The Cu electrode was placed in a 0.01 M solution of Cu(NO;)2, and the Ag electrode was placed in a 1.00 M solution of AGNO3. What is the Ecell for this voltaic cell? Assume the temperature is 298 K. Also NO; is a spectator ion. ( Select ) Voltmeter Ag Cu sat bridge AgNO= 1.00 M -0.01 M >arrow_forwardUse the standard reduction potentials located in the 'Tables' linked above to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: Ni?+ (aq) + Cd(s) → Ni(s) + Cd²+ (aq) Answer: kJ K for this reaction would be than one.arrow_forwardhelp please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forward
- please step by step solution.arrow_forwardEnter electrons as e". Use smallest possible integer coefficients. States are not required. If a box is not needed, leave it blank. Standard Reduction Potentials (Volts) at 25 °C Cl₂ (g) + 2 e →2 Cl(aq) O2(g) + 4 H3O+ (aq) + 4 e 6 H₂O(1) 1.360 1.229 2 H2O(l) + 2e Al3+ (aq) + 3 e → Al (s) H2(g) + 2 OH(aq) -0.828 -1.660 A 0.114 M neutral aqueous AlCl3 solution is electrolyzed under 1 atm pressure using platinum electrodes. (a) Write the half-reactions expected to occur, taking into account the effect of the non-standard conditions on the electrode potentials. Half-reaction at anode: + + + + Half-reaction at cathode: + + + + (b) What is the expected decomposition potential?arrow_forwardShown below are some standard reduction potentials. For which of these compounds is oxidation most favorable? (Imagine you mixed all four of these compounds together in equal quantities. Which one would get oxidized?) a) H2O b) NADH c) O2 d) NAD+arrow_forward
- Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy delta G^0 for the following redox reaction. I2(s) + 6H2O(l) + 5 Cl2(g) -> 2IO3-(aq) + 12H+(aq) + 10Cl-(aq)Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardUse standard reduction potentials to calculate the standard free energy change in kJ for the reaction: 2H+ (aq) + Hg(1)→ H₂(g) + Hg²+ (aq) 2H+ (aq) + 2e¯ → H₂(g) Fº red 2+ Hg2 (aq) + 2e¯ → Hg(1) AGO = || kJ K for this reaction would be Eº red = 0.000 V = = 0.855 V than one.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY