
Concept explainers
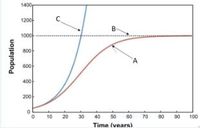
1. The diagram shows the population curve (y-axis) vs time (x-axis). Which line/curve best describes the theory of natural selection of Charles Darwin?
2. The diagram shows the population curve (y-axis) vs time (x-axis). Which curve represents the scenario described by Thomas Malthus "the populations with unlimited natural resources grow very rapidly, after which population growth decreases as resources become depleted".
3. The diagram shows the population curve (y-axis) vs time (x-axis). Which curve best represents the growth of bacteria?
4. The diagram shows the population curve (y-axis) vs time (x-axis). Which line/curve acts as a moderating force in the growth rate by slowing it when resources become limited and stopping growth once it has been reached.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- 1. Shown below are figures of the closed and open structures of the voltage gated potassium channel protein in the cell membrane of a neuronal cell. Extracellular CLOSED Extracellular OPEN Cytosol Region A Cytosol Region A Region A of the channel protein functions as a paddle. The paddles move up and down, opening and closing the central pore through which potassium ions flow. The resting membrane potential of a neuronal cell is -70mV. Action potential +40 The action potential graph is shown on the right, at what point in the graph or when would voltage gated potassium channels be closed and when would they be open? Choose from Resting, depolarization, repolarization or refractory period. Describe briefly. a. Threshold -55 Failed initiations Resting state -70 Stimulus 1 Refractory period b. Would potassium ions move in or out of the cell when the voltage gated potassium channels are open? 1 4. Time (ms) What kind/type of amino acids would be present in region A of the voltage gated…arrow_forwardBASED ON THIS GRAPH: A small community that is heavily infested with mosquitoes was sprayed weekly with the insecticide DDT for several months. Daily counts providing information on mosquito population size are represented in the graph below. Provide a biological explanation for the changes in the mosquito population over time. Use the terms: insecticide resistance/resistant, natural selection, favorable trait, reproduce, mutation/sexual reproductionarrow_forward21. What is an example of microevolution? Group of answer choices a.Anole lizards getting stickier feet to live in the city. b.The population of anoles being wiped out because of the city. c.The anoles lizards interbreeding with a different species of lizard.arrow_forward
- For questions 14-20, fill in the blanks using the word bank below. Fitness i Mejosis Mutations Evoludon Selected variation Competition allele frequency pressure 14. According to Darwin's theory of natural selection, every population has heritable their traits. mitosiss 15. These differences are caused by meiosis and 16. Predators, competition, changing environments will exert on individuals in a population. 17. Some traits will be beneficial and increase an organism's 18. Eventually favorable traits will be for, while hamful traits will not. 19. This will cause a shift in the of a population over time. 20. This shift in the genotypes and phenotypes of a population is known as low is a diagram demonstrating the effects of antibiotics on a population of bacteria over time. Draw a tch each box with its correct caption. 0. 000 24. 00 23. 22.arrow_forwardSeveral generations of population X have been studied. The dominant phenotype frequency for the second generation of population X was calculated to be 0.71. The tenth generation for population X has been collected and phenotyped and the dominant phenotype frequency was 0.50. Is population X evolving? Explain your answer. 3arrow_forwardSelect the best working definition for evolution: Change in species over time Change in genotype frequencies in individuals over time Change in genotype frequencies in a population over time Change in allele frequencies in a population over timearrow_forward
- Support your answer with Evidence: 5. What are some ways another kind of natural disaster could change an environment and change the selective pressures felt by a species? Support your answer with Evidence: 6. How does the scenario meet the conditions for natural selection? DELL F9 F10 F11 F6 F7 F8 Pr F4 F5 & $ 8. 7 8 Coarrow_forwardthanksarrow_forwardWhich of the following forces creates diversity? 1 - bottleneck effect 2- genetic drift 3 - mutation 4- natural selectionarrow_forward
- A hypothetical population has two alleles for an “A" gene: A1 and A2. The allele frequencies of the population were determined to be 70% A1 and 30% A2. What is the expected (predicted) frequency of zygotes with the A2A2 genotype (q2) if the population is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? O A. 0.42 O B. 0.49 O C.0.21 O D.0.09 QUESTION 4 A hypothetical population has two alleles for an "A" gene: A1 and A2. The allele frequencies of the population were determined to be 70% A1 and 30% A2. Geneticists collected DNA samples from 1,000 individuals within the population and found the actual (observed) genotype frequencies of the population to be: 22% A1A1, 59% A¬A2, and 19% A2A2. Is this population actually in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? (Note: if the actual/observed genotype frequecies are fairly close - within 5 or 10% of the expected/predicted frequencies, then consider them equal) O A. Yes O B. Noarrow_forward30. Which of the following tends to produce more heterozygous individuals in a population? Group of answer choices gene flow disassortive mating assortive mating genetic drift natural selectionarrow_forwardWhat are some notes or take aways about this model? Model 1 – PopGen Fish Pond This model is an agent-based population genetics simulation. The program contains the tools to conduct virtual experiments violating all the assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg theory (small population, selection, mutation, migration, and non-random mating).arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





