
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
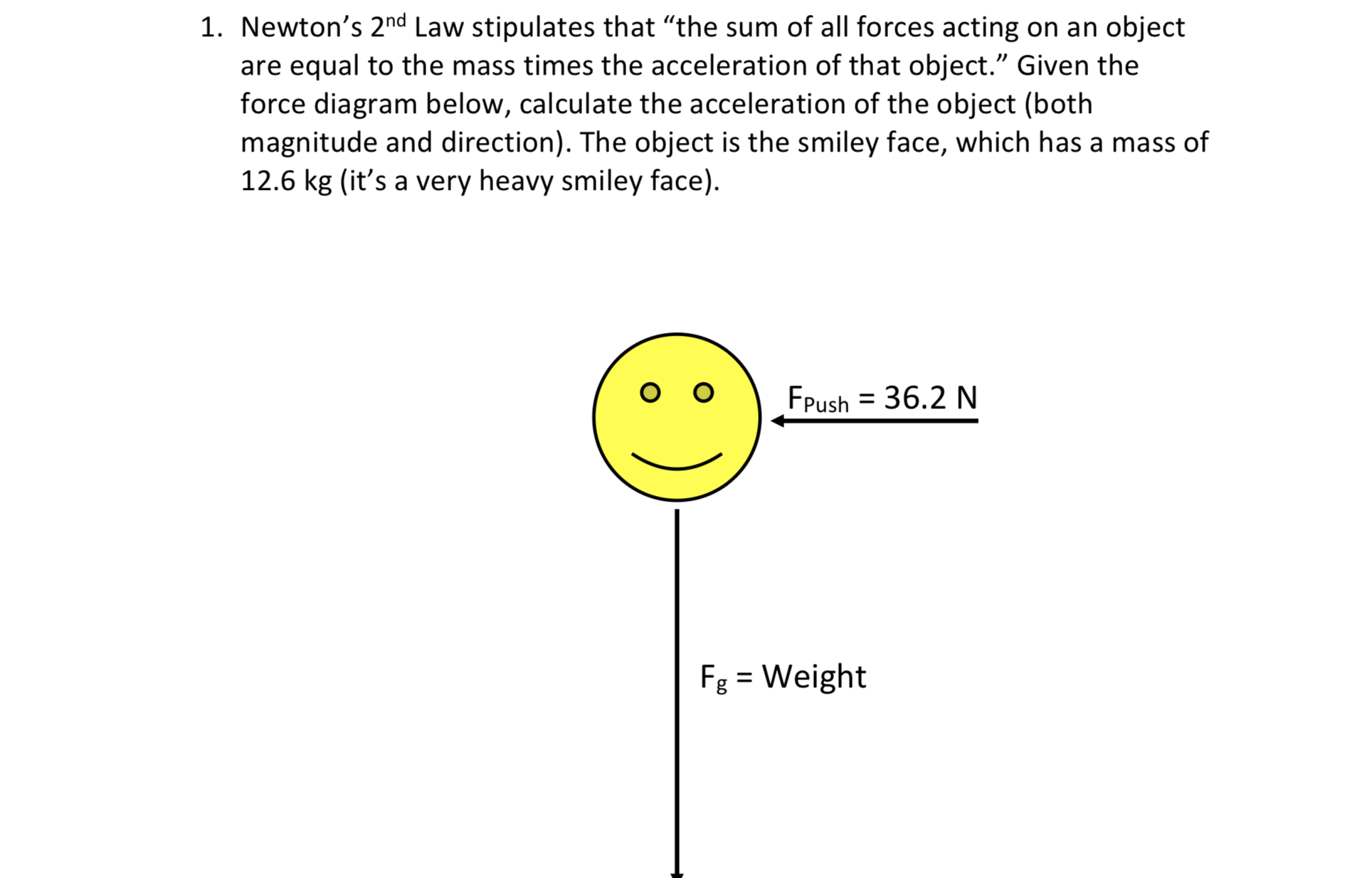
Transcribed Image Text:1. Newton's 2nd Law stipulates that "the sum of all forces acting on an object
are equal to the mass times the acceleration of that object." Given the
force diagram below, calculate the acceleration of the object (both
magnitude and direction). The object is the smiley face, which has a mass of
12.6 kg (it's a very heavy smiley face).
FPush = 36.2 N
%3D
Fg = Weight
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 14.8 lb object has the acceleration components a. - (06) + (075) , = (107)- (043"): 0.83 What is the magnitude of the net force Fnet acting on the object at time t = 4.07 s? Fnet 36.1 What is the direction of the net force at this same time? Give the answer as a number of degrees counterclockwise from the +x-аxis.arrow_forwardSuppose two children push horizontally, but in exactly opposite directions, on a third child in a wagon. The first child exerts a force of 75.0 N, the second a force of 90.0 N, and the mass of the third child plus wagon is 23.0 kg. Assume no friction in this problem. a. Draw a free-body diagram, including all forces acting on the wagon. b. Show the component equations (Fx and Fy) in terms of variables only. c. Calculate the acceleration.arrow_forward4. A block of mass m accelerates up a slope that has friction. a. Draw a free-body diagram for the block indicating all the forces acting on it. (Note that there must be a force acting on the block in order for it to accelerate up the slope.) b. Write down the equations for Newton's 2nd law for both x and y directions. c. Solve for the applied force Fap in terms of the angle of incline 0, mass m, acceleration of the block a, kinetic friction force fr, and acceleration of gravity g.arrow_forward
- 1.There is a falling object, whose mass is A [kg] and experiences a force (its own weight) equal numerically to A times 9.81. The object starts from rest and the air causes a retarding force numerically equal to B times its velocity. a)Find general expression for velocity as a function of time, and draw its graph. b)Evaluate velocity for t=C (s) Depending on your value of R choose A B R 0 1 2 6 8 0.180 0.200 0.220 Font C 4 5 6arrow_forward3. An object with a mass of 1500 g (grams) accelerates 10.0 m/s” when an unknown force is applied to it. What is the amount of the force?arrow_forward6. Two blocks, with masses shown are pulled up a ramp by a pull force P. The kinetic friction coefficient between each block and the ramp is µg = 0.40. The blocks start from rėst and speed up the ramp. They reach a speed of 0.85 m/s after 4.00 s. 4.0 kg a) Draw FBDS of both masses. Write down correct NII equations. Find the magnitude of the tension in the string connecting the two blocks. 6.0 kg 30°arrow_forward
- 2. A chain consists of identical links, each with a mass of 2.5 kg. You grab the top link and hold the chain at rest so that it hangs vertically. a) Draw a free body diagram of the bottom three links (labeled 1, 2, 3). Label all forces and use double subscript notation to denote which object exerts the force and which object is experiencing the force. b) Find the magnitude of the force exerted on link 1 by link 2, in Newtons. c) Find the magnitude of the force exerted on link 2 by link 3, in Newtons.arrow_forward6. A horizontal pull force of 35 N is required to just start a 6 kg box moving across a horizontal concrete floor. a) Draw the free-body diagram of the box, showing all of the forces acting on the box. b) What is the coefficient of static friction,μs, between the box and floor? c) The 35 N pull force continues, but now that the box is moving, it accelerates at constant a = 0.6 m/s². What is the coefficient of kinetic friction,μk?arrow_forwardBox A, weighting 60 N, is placed on a table tilted at angle of 15˚. Another box, B, weighing 40N, is placed on top of A. Both boxes are at rest.A) Draw the free-body diagram for box B. What is the frictional force exerted on A by B? B) Draw the free-body diagram for box A. What is the frictional force exerted on A by the table?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON