
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:1. Find all steady states of differential equationx5x24 and find stability.
2. Solve differential equation K(70-N) where ko o.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward

Step 1
Problem 1:
To find all steady states of the given differential equation.
Find all the equilibrium points by setting X\'=0.
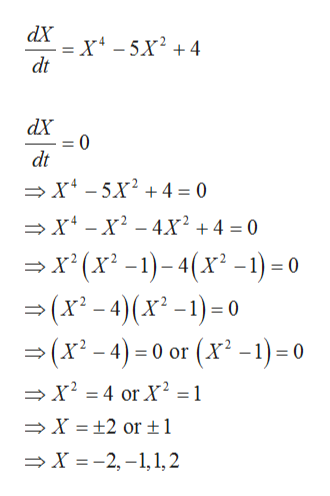
arrow_forward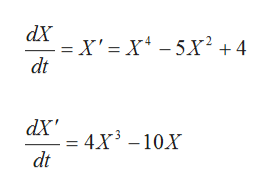

Step 2
Thus observe that the equilibrium points are X= -2, -1, 1, 2.
Find the derivative of X'.
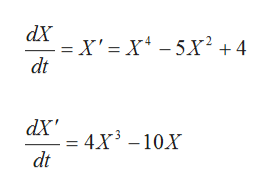
arrow_forward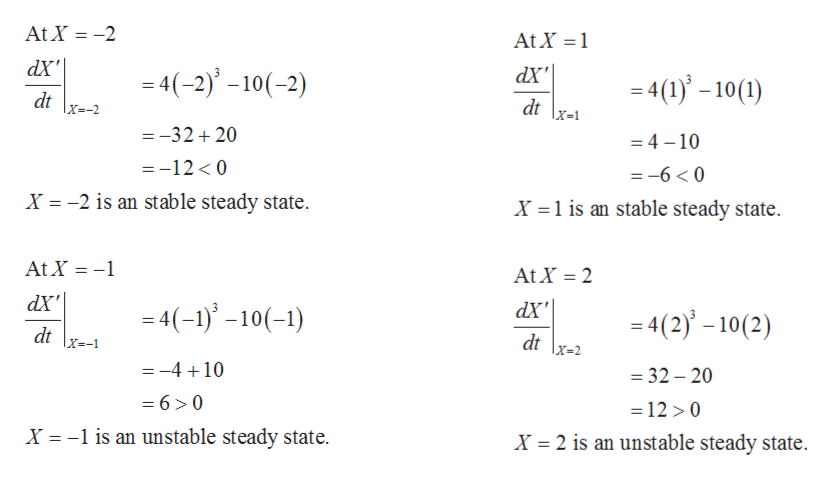

Step 3
Find (dX'/dt) at the equilibrium points.

Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Describe the qualitative behavior of the differential equation by locating all the equilibrium points (fixed points) and graphing the phase trajectory in the phase plane.arrow_forwardWhat is the order of the differential equation y"-3y + 6y-2y=0? Enter your answer as a numerical answer. For example, if the equation is seventh-order, then enter 7 as your answer.arrow_forwardThe population of fish in a lake grows logistically according to the differential equation where t is in years with no harvesting. If the lake has 550 fish and opens to fishing, determine how many fish can be harvested per year to maintain equilibrium. dy/dt=0.1y(1-y/2500) Differential Equationsarrow_forward
- Differential equations have been used extensively in the study of drug dissolution for patients given oral medications. The three simplest equations used are the zero-order kinetic equation, the Noyes-Whitney equation, and the Weibull equation. All assume that the initial concentration is zero but make different assumptions about how the concentration increases over time during the dissolution of the medication. The zero-order kinetic equation states that the rate of change in the concentration of drug c (in mg/mL) during dissolution is governed by the differential equation dc dt = k where k is a positive constant. Is this differential equation pure-time, autonomous, or nonautonomous? pure time autonomous nonautonomous State in words what this differential equation says about how drug dissolution occurs. The drug concentration increases linearly with time during dissolution. The drug concentration remains constant with time during dissolution. The drug concentration…arrow_forwardThe differential equation 14=dT/dt+0.017T models the temperature, T, above room temperature, of an electric burner. T is measured in degrees Fahrenheit and t is greater than or equal to zero is in seconds. Find the general solution of the differential equation in terms of a constant karrow_forwardSolve a) find the general solution for the given differential equations at least for i, ii, or iv.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning