
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
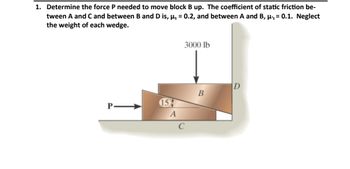
Transcribed Image Text:1. Determine the force P needed to move block B up. The coefficient of static friction be-
tween A and C and between B and D is, μs = 0.2, and between A and B, μ's = 0.1. Neglect
the weight of each wedge.
P
154
A
3000 lb
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. Rigid bar BEF is loaded, moving point F downward by 3mm. If the axial strain in bar DE is 400μ, what is the vertical displacement of point C? D 0.75m 0.5m A В 1. C E חח 0.5m 1.2m F 1 P 0.8marrow_forwardDetermine the slope and the displacement at the end C of the beam. E = 200 GPa, I = 70(106) mm4. Use the conjugate beam methodarrow_forwardDetermine the vertical displacement at point B (mm). The value of the beam ABCD varies linearly from El at the supports A and D to 1.5El at B and C respectively and is constant between B and C. El = 15.0 x 103 kNm2 %3D |20 kN B 20 kN 5f EI 1.SEI D ME 2EI El I.SEI VA 2.0 m 3.0 m 2.0 m 4.0 m 7.0 m 5.97 7.11 12.14 none of the abovearrow_forward
- The beam AD is loaded as shown. The coefficients of static friction at the wedge's top and bottom surfaces are µca = 0.25 and µcB = 0.35, respectively. Neglect the weight and size of the wedge and the thickness of the beam. Determine the horizontal force P which must be applied to the wedge in order to remove it from under the beam. 4 kN/m 10° D B 3 m 4 marrow_forwardA simply supported beam is subjected to a triangularly distributed load of Q = 7.6 kN/m, over segment length L/2 = 3.7 m and a mid-span moment of MO=7.6 kN-m. Determine the maximum slope and deflection of the beam. Assume El is constant. A QkN/m 1/12 - Mo B 7/2 6 Carrow_forwardDetermine the force P required to force the 11° wedge under the 95-kg uniform crate which rests against the small stop at A. The coefficient of friction for all surfaces is 0.39. 8° Answer: P = 11° i 1.8 m 95 kg 0.6 m A 11° Narrow_forward
- 13 kN B Block A supports a pipe column and rests as shown on wedge B. Knowing that the coefficient of static friction at all surfaces of contact is 0.25 and that 0=45°, determine the smallest force P for which equilibrium is maintained.arrow_forward5. Blocks A, B, and C have weights of 50 N, 25 N, and 15 N, respectively. Determine the smallest horizontal force P that will cause impending motion. The coefficient of static friction between A and B is 0.3, between B and C is 0.4, and between block C and the ground is 0.35. : P=45 N→ 52arrow_forwardk=2 lb/ft -¨¨¨¨¨ B Two blocks A and B have a weight of 11 lb and 6 lb, respectively. They are resting on the incline for which the coefficients of static friction are μA = 0.16 and μB = 0.23. Determine the angle 0 which will cause motion of one of the blocks. What is the friction force under each of the blocks when this occurs? The spring has a stiffness of k = 2 lb/ft and is originally unstretched. Determine the smallest angle which will cause motion of one of the blocks. Determine is the friction force under the block A at this angle. Determine is the friction force under the block Bat this angle.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning