
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
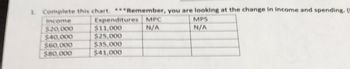
Transcribed Image Text:1. Complete this chart. ***Remember, you are looking at the change in income and spending. (
Income
$20,000
$40,000
$60,000
$80,000
Expenditures MPC
N/A
$11,000
$25,000
$35,000
$41,000
MPS
N/A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain the impact of the change in consumer's income on the demand of goods and services.arrow_forwardEconomics 2a-c answer ++++rating A consumer is initially at point A on her original budget constraint (the thin solid line with the Xintercept and Y-intercept labeled). She experiences a change in her budget constraint and is now at point B. Her new budget constraint is shown by the dotted line. C2 [(Y1 + Aj)(1+r) +Y2]/Pz U2 [Y, + A, + (Y2/(1+r))]/Pel C, a. What appears to have been the cause of the change in her budget constraint? b. Is the substitution effect positive or negative? Show this effect (draw an arrow on the graph). c. Is the income effect positive or negative? Show this effect (draw an arrow on the graph).arrow_forward7 At high levels of disposable income Multiple Choice both the APC and APS are high. both the APC and APS are low. the APC is high and the APS is low. the APC is low and the APS is high.arrow_forward
- consumer's expenditure minimization problem explain in detail both theoretically and practically ?arrow_forward10. Suppose tangerines are an inferior good. This means that if your income tangerines. decreases, you will buy (more/fewer)arrow_forward2. A consumer has and income of £40 to spend in two commodities. Commodity 1 costs £10 per unit, and commodity 2 costs £5 per unit. (i) What is the consumer's budget equation? If the consumer spends on his/her money on commodity 1, how much could he/she buy? Suppose the consumer was initially consuming 2 units of commodity 1 and 4 units of commodity 2. If the price of commodity 1 increases to £20 and the price of commodity 2 remains £5, by how much would the consumer's income have to rise so that he can still afford the initial bundle? (ii) Now suppose this consumer is a rational consumer and would like to maximize his/her utility. Explain how an increase in income will affect the consumer's optimal consumption bundle?arrow_forward
- Sarah has a budget of 58. Her utility function if U(x,y) = x*y. %3D The price of good x is 1, the price of good y is 8. How many units of good x does Sarah consume? Answer: Type here to search 01/arrow_forwardCan i get some help please?arrow_forwardSolve it correctly please. I will rate accordingly.arrow_forward
- Please see attachment and type out the correct step by step answer with proper explanation of it within 40 50 minutes. Will give you thumbs up only for the correct answer. Thank you .arrow_forwarde the information in the table to answer the folowing qustiona. Al numbers are in bilions of 2012 dolars Govermment Purchases (G) $2.00 $2.500 $2.500 $2.500 $2.500 Pianned investment ( $1.000 Net Exports (NK) Real GOP (Y) Consumption (C) $12.000 $13.000 $14,000 $15.000 $10.000 $9.500 $10.250 $1.000 -$500 -$500 -5500 -$500 -$500 $1.000 $1,000 S11,750 $1.000 $12.500 $1.000 The equibrum level of GOP is S bilion The MPC is (snter your reaponse to two decimal places) Suppose that net exporta increase by $200 blion. Using the multiplier formua, determine the new level of GOP. AS200 bilon increase in net exports leads to a change in spending of S bilion, so the new level of GDP wi be billonarrow_forward(Table: Marginal Utility per Dollar of Twix) Use Table: Marginal Utility per Dollar of Twix. The price of Twix is $2 per bar. If the price of Twix increases to $3 per bar, the marginal utility per dollar for each bar of Twix will: Table: Marginal Utility per Dollar of Twix Bars Quantity of Twix bars Total utility 10 0 1 6 2 10 3 13 15 16 5 O remain constant. O increase O decrease. O fluctuate randomly.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education