
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
1. Carefully analyze Tables 2, 3, 4 & 5, and answer the following question. In this study, one exposed group is people who are in the 15-24 age group and had the recent stressor of mental illness. What is the unexposed group for this example?
2. In terms of suicide risk, which stressors affect the elderly (65+) more than other age groups?
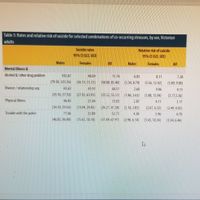
Transcribed Image Text:Table 5: Rates and relative risk of suicide for selected combinations of co-occurring stressors, by sex, Victorian
adults
Suicide rates
Relative risk of suicide
95 % a (LC, UCI)
95% C (LCI, UCI)
Males
Females
All
Males
Females
All
Mental illness &
Alcohol &/ other drug problem
102.67
40.69
71.74
6.85
8.31
7.28
(79 59, 125.76)
(26.13, 55.25)
(58.08, 85.40)
(5.34, 8.79)
(5.56, 12.42)
(5.89, 9.00)
Divorce / relationship sep.
43.63
45.93
44.51
2.60
9.06
4.13
(29.76, 57.50)
(27.92, 63.93)
(33.52, 55.51)
(1.86, 3.63)
(5.88, 13.94)
(3.17,5.36)
Physical illness
46.83
21.44
33.83
2.87
4.11
3.17
34.10, 59.56)
(13.04. 29.85)
26.27, 41.38)
(2.14, 3.83)
(2.67,6.33)
(2.49,4.03)
Trouble with the police
71.66
32.88
52.73
4.28
5.96
4.78
(46.83, 96.48)
(15.65, 50.10)
37.49,67.97)
(2.98, 6.14)
(3.43, 10.34)
(3.54,6.46)

Transcribed Image Text:Table 2: Exposure to stressors in the 12-months prior to suicide, suicide rates and relative risk of suicide, by age
group, Victorian adults
15-24 years
25-44 years
45-64 years
65+ years
ALL
Suidide rate per 100,000
95% C (LCI, UCI)
Mental illness
27.23
31.21
44.75
74.31
38.45
(16.96, 37.51)
(25.13,37.30)
(35.89, 53.61)
(52.10, 96.52)
(33.86, 43.05)
Relative risk
95% CI (LCI, UCI)
Mental illness
4.75
4.71
4.95
15.31
5.39
(2.90, 7.78)
(3.55, 6.25)
(3.77,6.50)
(10.10, 23.20)
(4.57, 6.37)
Table 3: Exposure to stressors in the 12-months prior to suicide, suicide rates and relative risk of suicide, by age
group, Victorian adult males.
15-24 years
25-44 years
45-64 years
65+ years
ALL
Suidde rate per 100,000
95% a (LCI, UCI)
Mental illness
64.86
43.54
86.73
91.86
61.64
35.70, 94.03)
33.19, 53.88)
(65.81, 107.66)
(55.85, 127.87)
(52.58, 70.69)
Relative risk
95% CI (LCI, UCI)
Mental illness
7.53
(4.25, 13.32
3.98
6.14
10.91
5.35
(2.87,5.52)
(4.46, 8.45)
(6.59, 18.07)
(4.40, 6.50)
Table 4: Exposure to stressors in the 12-months prior to suicide, suicide rates and relative risk of suicide, by age
group, Victorian adult females.
15-24 years
25-44 years
45-64 years
65+ years
ALL
Suicide rate per 100,000
95% a (LCI, UCI)
11.45
(B.52, 19.39)
Mental illness
19.71
22.39
58.73
22.15
(12.99, 26.44)
(14.63, 30.15)
(31.60, 85.86)
(17.60, 26.70)
Relative risk
95% CI (LCI, UCI)
Mental illness
4.96
8.47
6.22
36.43
8.39
(1.80, 13.68)
(4.66, 15.39)
(B.58, 10.78)
(15.84, 83.79)
(5.97, 11.80)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. The scores for 15 persons on the Stressful Life Events Inventory (SLEI) and the scores for 15 other persons on the Major Stressors Questionnaire (MSQ) are presented in the Assessment 3 Data Excel file in the Stress Scores tab. For both surveys, higher scores mean that the person has experienced more stressors recently, suggesting a greater risk for stress-related symptoms such as acute anxiety attacks. Open the Assessment 3 Data Excel file and look over the SLEI and MSQ raw scores and z-scores in the Stress Scores tab. A. Please take a look at Participant 8 and 23 raw scores and z-scores. Who is at the greatest risk for acute anxiety attacks, Participant 8 or 23? Please make sure to briefly explain your answer based on the z- scores. B. What is the probability that someone will score higher than 40 on the SLEI? Is this unusual? Why or why not? What is the probability that someone will score higher than 125 on the MSQ? Is this unusual? Why or why not? (Please make sure to look up…arrow_forwardIn a survey of families in which both parents work, one of the questions asked was, “Have you refused a job, promotion, or transfer because it would mean less time with your family?” A total of 200 men and 200 women were asked this question. “Yes” was the response given by 29% of the men and 24% of the women. Based on this survey, can we conclude that there is a difference in the proportion of men and women responding “yes” at the 0.05 level of significance?arrow_forward1. State whether it will experimental or observational 2. If observational, identify which type specifically (retrospective cohort, prospective cohort, case-control, cross-sectional, ecological) 3. Briefly explain how you can tell what type of study it is. In 2010, we examined the medical records of 2,000 patients ages 53+ associated with Kaiser Permanente (large health care organization) who did NOT have kidney disease in 2005. Then, we look back in the records to see who took BZDs from 2000-2005. After that, we look to see who developed kidney disease from 2006 until 2008. We compared the rates of kidney disease among those who took the BZDs and those who didn’t.arrow_forward
- 4. Data from the year 2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) survey includes laboratory measurements on a random sample of more than four-thousand 18 - 65 year old persons in the United States. The following boxplots display the distribution of blood lead levels (mg/dL) for this sample, separately for males and females. The accompanying tables display summary statistics of the sample values. Blood Lead Levels by Biological Sex NHANES Laboratory Data, 2012 Females (n=2,128) Males (n=1,892) 20 i: 1.27 Î: 1.97 s: 1.61 Range: 0.18 -22.3 s: 1.16 Range: 0.18 – 15.2 Percentiles: 5h: 0.60 25th: 1.00 Percentiles: 5h: 0.37 25: 0.62 50: 0.95 50: 1.60 75th: 1.5 75th: 2.4 95: 3.10 95h: 4.6 Blood Lead Level (micrograms/dl) 15 O O HOOD O CaO OD O 0arrow_forward2.- The journal Behavioral Research in Accounting published a study of Machiavellian traits in accountants. Machiavellian describes negative character traits that include manipulation, cunning, duplicity, deception, and bad faith. A questionnaire by email was administered to a random sample of 700 accounting alumni of a large southwestern university; however, due to nonresponse and incomplete answers, only 198 questionnaires could be analyzed. Several variables were measured, including age, gender, level of education, income, job satisfaction score, and Machiavellian (“Mach") rating score. The research findings suggest that Machiavellian behavior is not required to achieve success in the accounting profession. a) What is the populatidn of interest to the researcher? Answer: Business accountants in the southwest Accountants in general Accounting alumni from this university Business alumni from this university b) What inference was made by the researcher? Answer: Accountants are always…arrow_forward5. In the United States, there is a strong relationship between education and smoking: well-educated people are less likely to smoke. Does a similar relationship hold in France? To find out, researchers recorded the level of education and smoking status of a random sample of 459 French men aged 20 to 60 years.36 The two-way table below displays the data. Is there convincing evidence of an association between smoking status and educational level among French men aged 20 to 60 years? Smoking Status Nonsmoker Former Moderate Heavy Primary School 56 54 41 36 Education Secondary School 37 43 27 32 University 53 28 36 16arrow_forward
- 1. College students Suppose a recent study of 1,000 college students in the U.S. found that 8% of them do not use Facebook. Which of the following describes the population for this example? 2. A survey question that starts out with the phrase “Do you agree that...” is an example of what? 3. Which of the following defines what is meant by a control group in an experiment? 4. Which of the following studies can result in researchers extending the results inappropriately because the sample doesn’t represent the intended population?arrow_forwardThe following is based on information from The Wolf in the Southwest: The Making of an Endangered Species, by David E. Brown (University of Arizona Press). Before 1918, the proportion of female wolves in the general population of all southwestern wolves was about 50%. However, after 1918, southwestern cattle ranchers began a widespread effort to destroy wolves. In a recent sample of 37 wolves, there were only 11 females. One theory is that male wolves tend to return sooner than females to their old territories, where their predecessors were exterminated. Do these data indicate that the population proportion of female wolves is now less than 50% in the region? Use α = 0.01. (a) What is the level of significance? State the null and alternate hypotheses. O Ho: P 0.5 O Ho: P = 0.5; H₁: p 5 and nq > 5. O The Student's t, since np > 5 and ng > 5. The standard normal, since np < 5 and nq < 5. O The Student's t, since np < 5 and nq < 5. What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round…arrow_forward1) a.What is/are the appropriate measure(s) of central tendency for each of the variables in Columns B-F? Explain your answers in no more than two sentences each. b. Calculate the measures of central tendencies above c. Imagine that a 21st run is added to your dataset. See the table below for its data Run Eth. Gly. Acid. Temp pH 21 18.2 7.2 2.1 18 4.2 d. Do these data points change your choices of central tendency reported in Question 2b? Explain your answer. Attached dataset; a b c d e f Run Ethanol Glycerol Acidity Temp pH 1 4.8 3.5 0.84 24 3.8 2 9.6 7.3 0.27 24 3.8 3 10.2 7.2 0.27 24 3.8 4 8.5 5.1 0.55 24 3.8 5 7.3 3.2 0.68 24 3.1272 6 4.8 1.2 1.24 30 4.2 7 7.9 4.4 0.65 18 3.4 8 6.7 4.3 0.65 30 3.4 9 9.8 6.9 0.47 24 3.8 10 10.2 7.2 0.32 24 3.8 11 9.8 5.8 0.51 24 3.8 12 10.2 7.5 0.28 24 3.8 13 8.2 5.1 0.49 18 4.2 14 7.1 3.9 0.6 18 3.4 15 8.2 4.8 0.46 13.908 3.8 16 5.6 3.3…arrow_forward
- "Bullying." according to noted expert Dan Olweus, "poisons the educational environment and affects the learning of every child." Bullying and victimization are evident as early as preschool, with the problem peaking in middle school. Suppose you are interested in the emotional well-being of not only the victims but also bystanders, bullies, and those who bully but who are also victims (bully-victims). You decide to measure depression in a group of victims and a group of bully-victims using a 26-item, 3-point depression scale. Assume scores on the depression scale are normally distributed and that the variances of the depression scores are the same among victims and bully-victims. The group of 25 victims scored an average of 25.3 with a sample standard deviation of 9 on the depression scale. The group of 23 bully-victims scored an average of 20.5 with a sample standard deviation of 8 on the same scale. You do not have any presupposed assumptions about whether victims or bully-victims…arrow_forwardI need help with 7, 8 and 9arrow_forward4. Straight As now, healthy later A study by Pamela Herd of the University of Wisconsin-Madison found a link between high-school grades and health. Analyzing data from the Wisconsin Longitudinal Study, which has tracked the lives of thousands of Wisconsin high-school graduates from the class of 1957, Herd found that students with higher grade-point averages were more likely to say they were in excellent or very good health in their early 60s. Does this mean people will live healthier lives if they increase their GPA? Explain.47arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman