
Micro Economics For Today
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337613064
Author: Tucker, Irvin B.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
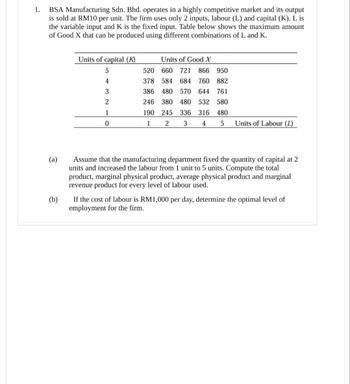
Transcribed Image Text:1.
BSA Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. operates in a highly competitive market and its output
is sold at RM10 per unit. The firm uses only 2 inputs, labour (L) and capital (K). L is
the variable input and K is the fixed input. Table below shows the maximum amount
of Good X that can be produced using different combinations of L and K.
(a)
(b)
Units of capital (K)
5
Units of Good X
520 660 721 866 950
4
378 584 684
760
882
3
386 480 570 644 761
2
246 380
480 532 580
1
190 245
336 316 480
0
1
2
3
4
5
Units of Labour (L)
Assume that the manufacturing department fixed the quantity of capital at 2
units and increased the labour from 1 unit to 5 units. Compute the total
product, marginal physical product, average physical product and marginal
revenue product for every level of labour used.
If the cost of labour is RM1,000 per day, determine the optimal level of
employment for the firm.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the marginal cost associated with producing three units of the contral variable, O (identify point E in the tablej? 36 Total Total Costs Benefits Benefit Net Marginal Marginal Narginal Net Bеnefit Control variable Benefits Cost MB(0) MC (Q) MND (0) Sepped B(Q) C(0) 900 100 800 900 100 800 2 1,700 300 800 200 600 2,400 600 1,800 700 E 400 4 1,000 2,000 600 400 200 3,500 1,500 2,000 500 500 600 1,800 1,400 3,900 2,100 D -200 4,200 4,400 2,800 300 700 -400 200 100 800 800 -600 4,500 4,500 900 -800 10 4,500 5,500 -1,000 1,000 -1,000 Mutiple Choice 50 100 200 300arrow_forwardWhat is the total cost associated with producing eight units of the control varlable, a (identify point B in the tablej? 34 Marginal Harginal Harginal Net Bеnefit Control Total Net Costs Benefits Benefit Total variable Benefits Cost Sepped B(Q) C(Q) MB(0) MC(0) MND (0) 900 100 800 900 100 800 2 1,700 300 800 200 600 2,400 600 1,800 700 E 400 1,000 1,500 400 500 2,000 2,000 1,800 1,400 4 600 200 3,500 500 3,900 2,100 D 600 -200 4,200 4,400 4,500 2,800 300 700 -400 800 200 800 -600 4,500 100 900 -800 10 4,500 5,500 -1,000 1,000 -1,000 Mutiple Choice 3,000 3,600 3,800 4,200arrow_forwarddo fast i will 5 upvotes.arrow_forward
- What is the marginal benefit associated with producing sx units of the control variable, O (identify point Din the table)? 35 Total variable Benefits Marginal Marginal Marginal Net Benefit Control Total Net Costs Benefits Benefit Cost Sepped B(Q) C(Q) N(Q) MB(Q) MC(Q) MNB (Q) 1. 900 100 800 900 100 800 2 1,700 300 800 200 600 3 2,400 600 1,800 700 E 400 4 1,000 2,000 600 400 200 3,500 1,500 2,000 500 500 6. 3,900 2,100 1,800 D 600 -200 4,200 2,800 1,400 300 700 -400 4,400 B 200 800 -600 008 4,500 4,500 100 900 -800 10 4,500 5.500 -1,000 1,000 -1,000 Mutiple Choice 600 400 200 100arrow_forwardCompleted 58 out of 60 uestion 31 of 60 If output falls below equilibrium, marginal cost will be higher than the price. O True O False LEGOarrow_forwardOutput TFC TVC TC MC ATC A 25 25 ---- -- ------- 1 25 25 50 25 50 C 2 25 40 65 32.5 3 25 70 95 E 4 25 110 33.75 F 5 25 160 50 What is the marginal cost of the 2nd unit of output? Cannot be determined. 15 25 30 O O O Oarrow_forward
- COST PER UNIT LRATC OTX Y Z OUTPUT According to the diagram above, output OY represents the firm's: Select one: O a. market potential O b. break-even point O c. minimum physical product O d. technical optimum plant sizearrow_forwardOutput TFC TVC TC MC ATC A 25 25 В 1 25 25 50 25 50 C 2 25 40 65 32.5 3 25 70 95 E 25 110 33.75 F 5 25 160 50 What is the marginal cost of the 4th unit of output? 40 25 50 Cannot be determined.arrow_forwardGomez runs a small pottery firm. He hires one helper at $12000 per year, pays annual rent of $5000 for his shop and spends $20000 per year on materials. He has $40000 of his own funds invested in equipment that could earn him $4000 per year if alternatively invested. he has been offered $15000 per year to work as a potter for a competitor. He estimates his entrepreneurial talents are worth $3000 per year. Total annual revenue from pottery sales is $72000. calculate the accounting profit and economic for Gomez pottery firm.arrow_forward
- 4arrow_forward(10) The law of diminishing returns states that: (a) as a firm uses more of a variable resource, given the quantity of fixed resources, the average product of the firm will increase. (b) as a firm uses more of a variable resource, given the quantity of fixed resources, marginal product of the firm will eventually decrease. (c) in the short run, the average total costs of the firm will eventually diminish. (d) in the long run, the average total costs of the firm will eventually diminish.arrow_forwardIIT Ball Bearings Inc. faces costs of production as follows: Quantity Total Fixed Cost Total Variable Cost 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 1 50 70 90 140 200 360 3 4 5 (A) Calculate the company's average fixed costs, average variable costs, average total costs, and marginal costs. (B) The price of a case of ball bearings is $50. Seeing that she can't make a profit, the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) decides to shut down Operations. What are the firm's profits/ losses? Was this a wise decision? Explain. (C) Vaguely remembering his introductory economics course, the Chief Financial Officer Tells the CEO it is better to produce 1 case of ball bearings, because marginal revenue equals marginal cost at that quantity. What are the firm's profits/losses at that level of production? Was this the best decision? Explainarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you


 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning



Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning