
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
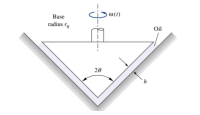
A solid cone of angle 2Ɵ, base r 0 , and density ρ c is rotating with initial
angular velocity ω 0 inside a conical seat,
as shown below. The clearance h is filled with oil
of viscosity μ. Neglecting air drag, derive an analytical expression for the
cone’s angular velocity ω(t) if there is no
applied torque.
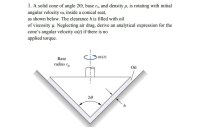
Transcribed Image Text:1. A solid cone of angle 20, base ro, and density p. is rotating with initial
angular velocity mo inside a conical seat,
as shown below. The clearance h is filled with oil
of viscosity u. Neglecting air drag, derive an analytical expression for the
cone's angular velocity o(t) if there is no
applied torque.
@(t)
Base
radius ro
Oil
20
h
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 17 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A solid cone of angle 2θ , base r 0 , and density ρ c is rotatingwith initial angular velocity ω 0 inside a conical seat, asshown in Fig. . The clearance h is fi lled with oil ofviscosity μ . Neglecting air drag, derive an analyticalexpression for the cone’s angular velocity ω ( t ) if there isno applied torque.arrow_forwardIn studying sand transport by ocean waves, A. Shields in1936 postulated that the threshold wave-induced bottomshear stress τ required to move particles depends on gravityg , particle size d and density ρ p , and water density ρ andviscosity μ . Find suitable dimensionless groups of thisthe problem, which resulted in 1936 in the celebrated Shieldssand transport diagram.arrow_forwardBy using the expression for the shear stress derived in class (and in BSL), show that the shear force on asphere spinning at a constant angular velocity in a Stokes’ flow, is zero.This means that a neutrally buoyant sphere (weight equal buoyancy force) that is made to spin in aStokes’ flow, will neither rise nor fall, nor translate in any preferential direction in the (x-y) plane. expressions for velocity are: v_r (r,θ)= U_∞ [1-3R/2r+R^3/(2r^3 )] cosθ v_θ (r,θ)= -U_∞ [1-3R/4r-R^3/(4r^3 )] sinθ Where v_r and v_θ are the radial and angle velocity, U_∞ is the velocity of fluid coming to sphere which very faar away from the sphere. And R is the radius of sphere.arrow_forward
- 3.14. Find the vorticity in polar coordinates for the following velocity com- ponents (a) v=rsin 0, ve = 2r cos 0 (b) v = cos 0, 11=0arrow_forwardA cube of side (a) and mass (M) is initially sitting fully submerged at the bottom of a container filled with a liquid of kinematic viscosity v and density p. The container has a square cross-section of side (a+a/5) and the cube is sitting right at the middle of the container base. (a) A force (F) starts pulling the cube up at a constant velocity (U). Develop an expression for the force in terms of (U, M. a. g, p and v). You may assume that the velocity in the gap between the cube's sides and the container walls is linear. The expression for (F) is to be valid as long as the cube remains submerged. (b) After the cube reaches the water surface, it continues to be pulled up by the same force. Develop a differential equation for the variation with time of the fraction of the cube that is submerged in water.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY