
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
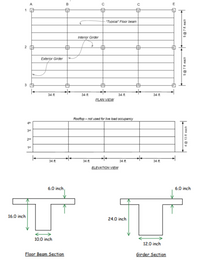
![1. (a) Calculate the tributary area, AT, for column 2A in the 4th floor (i.e. the column supporting the roof) to be used
in calculation of total roof live load on column 1A (note that "roof live load" is different than "floor live load").
(b) Calculate the tributary area, AT, for column 1A in the 2nd floor to be used for calculation of floor live load
acting on the column.
c) Calculate the tributary area, AT, for column 1B in the 1st floor to be used for calculation of floor live load
acting on the column.
(d) Calculate the influence area, AI, for column 1B in the 1st floor for floor live load.
e) For a specified live load of p. = 40 psf, calculate the design floor live load, pz [psf], for column IB in the Ist
floor using floor live load reduction from code (if allowed).
() Using your answers from (c) through (e), calculate the axial force, P. [kip], acting at the top of column 1B in
the Ist floor due to floor live load.
(g) If columns are 16 in. x 16 in. in x-sect, typical floor beams are 10 in. wide and 16 in. deep in x-sect., girders are
12 in. wide and 24 in. deep in x-sect, and the floor slab is 6 in. in thickness, calculate the axial dead load due to
column, girder, beam, and slab weight acting at the top of column 1B in the first floor. Assume all of these
elements are reinforced concrete with a unit weight of 150 lbs/ft³. Then calculate the factored axial load at the top
of the column including both dead and live loads and the U = 1.2D + 1.6L load combination.
2. (a) Calculate the tributary width for a "typical" floor beam (see figure for "typical floorbeam').
(b) Caleulate AT for a typical floor beam.
(c) Calculate the influence area, AI, for a typical floor beam.
(d) For the code specified live load of po = 40 psf, calculate the design floor live load, pL [psf], for a typical floor
beam using live load reduction (if permitted).
(e) Calculate the uniformly distributed load, wL (plf], acting on a typical floor beam due to floor live load.
(1) Calculate the tributary width of exterior girder 2A-3A, the tributary area, AT, the influence area Al, and the
design floor live load, pL (psf] using live load reduction (if permitted).
(g) Calculate and draw (show a simply supported beam and the live loads acting on it) the live load acting on an
exterior girder (e.g. 2A – 3A) using the design floor live load determined in f) above.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/59f58f32-7539-4361-aa58-6ce55f60f85f/aecd929b-fb3b-41f6-badd-a08a1b4a525b/4int92h_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:1. (a) Calculate the tributary area, AT, for column 2A in the 4th floor (i.e. the column supporting the roof) to be used
in calculation of total roof live load on column 1A (note that "roof live load" is different than "floor live load").
(b) Calculate the tributary area, AT, for column 1A in the 2nd floor to be used for calculation of floor live load
acting on the column.
c) Calculate the tributary area, AT, for column 1B in the 1st floor to be used for calculation of floor live load
acting on the column.
(d) Calculate the influence area, AI, for column 1B in the 1st floor for floor live load.
e) For a specified live load of p. = 40 psf, calculate the design floor live load, pz [psf], for column IB in the Ist
floor using floor live load reduction from code (if allowed).
() Using your answers from (c) through (e), calculate the axial force, P. [kip], acting at the top of column 1B in
the Ist floor due to floor live load.
(g) If columns are 16 in. x 16 in. in x-sect, typical floor beams are 10 in. wide and 16 in. deep in x-sect., girders are
12 in. wide and 24 in. deep in x-sect, and the floor slab is 6 in. in thickness, calculate the axial dead load due to
column, girder, beam, and slab weight acting at the top of column 1B in the first floor. Assume all of these
elements are reinforced concrete with a unit weight of 150 lbs/ft³. Then calculate the factored axial load at the top
of the column including both dead and live loads and the U = 1.2D + 1.6L load combination.
2. (a) Calculate the tributary width for a "typical" floor beam (see figure for "typical floorbeam').
(b) Caleulate AT for a typical floor beam.
(c) Calculate the influence area, AI, for a typical floor beam.
(d) For the code specified live load of po = 40 psf, calculate the design floor live load, pL [psf], for a typical floor
beam using live load reduction (if permitted).
(e) Calculate the uniformly distributed load, wL (plf], acting on a typical floor beam due to floor live load.
(1) Calculate the tributary width of exterior girder 2A-3A, the tributary area, AT, the influence area Al, and the
design floor live load, pL (psf] using live load reduction (if permitted).
(g) Calculate and draw (show a simply supported beam and the live loads acting on it) the live load acting on an
exterior girder (e.g. 2A – 3A) using the design floor live load determined in f) above.
Transcribed Image Text:A
B
1
Турсаг Fioor bеam
Interior Girder
中
2
Exterior Girder
34 ft.
34 ft.
34 t
34 ft.
PLAN VIEW
Rooftop - not used for ive load occupancy
2
1
34t.
34
34 R.
34
ELEVATION VIEW
6.0 inch
6.0 inch
16.0 inch
24.0 inch
10.0 inch
12.0 inch
Floor Beam Section
Girder Section
5@7t each
5@7A each
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QL10arrow_forwardProblem A barge shown supports the load W1 and W2 for every one-meter strip along the longitudinal section. W1 = 160 kN/m W2 = 291 kN/m L1 = 3 m L2 = 7.8 m L3 = 3.5 m W₁= w₁ kN/m W₂= W² kN/m CHILD ATHIB А q kN/m + L1 L3 L Find the pressure "q" so that the upward pressure is uniform and that the barge remains horizontal. (kN/m) L2 Earrow_forwardA swimming pool has a width of 4m and a side profile as shown. Determine the magnitude that the water exerts on walls AB and DC, and the bottom BC using the general solution of hydrostatic force. Show complete and detailed solution with FBD.arrow_forward
- The second floor of a light manufacturing building is constructed from a 125 mm thick stone concrete slab with an added 100 mm cinder concrete as shown. If the suspended ceiling of the first floor consists of metal lath and gypsum plaster, determine the dead load for design in kN per square meter of the floor area. 125 mm concrete slab ceiling 100 mm cinder concrete ANS. 5.055 kN/m²arrow_forwardA vertical triangular gate with a horizontal top base that is 3m wide is 6m high. It is submerged in oil having a sp. gr. of 0.82 with its top base 2.5m below the fluid surface. Determine the location from the fluid surface in m of the total hydrostatic pressure acting on one side of the gate.arrow_forwardP2.15) Determine the dead load and live load for the second floor of a library in which any area can be used for stacks. Assume that there will be a steel channel ceiling system (2 psf) and asphalt tile on the floors. The floors are 6-in. reinforced concrete. Allowance should be provided for mechanical ducts.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning