
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079250
Author: Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Please solve
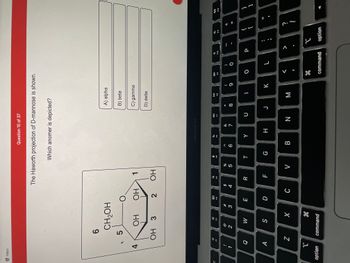
Transcribed Image Text:### Understanding D-Mannose Anomers
**Question 10 of 37**
The Haworth projection of D-mannose is shown below.
**Which anomer is depicted?**
#### Haworth Projection Diagram
A cyclic structure of D-mannose is depicted in Haworth projection. The carbon atoms in the ring are numbered clockwise from the anomeric carbon (1) to the end of the ring at carbon (5). The CH2OH group is attached to carbon (5). The OH groups are arranged as follows:
- Carbon 1 (anomeric carbon) has an OH group down.
- Carbon 2 has an OH group up.
- Carbon 3 has an OH group down.
- Carbon 4 has an OH group down.
The molecule represented is β-D-mannose because the OH group on the anomeric carbon (Carbon 1) is oriented downward in the Haworth projection.
**Possible Anomer Options:**
- A) alpha
- B) beta
- C) gamma
- D) delta
The correct answer is **B) beta**.
**Note:** The alpha and beta anomers differ in the position of the OH group attached to the anomeric carbon (carbon 1). In the alpha anomer, the OH group is on the opposite side (down) compared to the CH2OH group attached to carbon 5. In the beta anomer, the OH group is on the same side (up).
This distinction is crucial in carbohydrate chemistry, influencing the stereochemistry and biochemical properties of sugars.
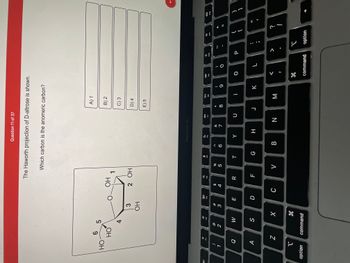
Transcribed Image Text:**Question 11 of 37**
The Haworth projection of D-altrose is shown.
Which carbon is the anomeric carbon?
*Image description:*
The image shows the Haworth projection of D-altrose, a cyclic structure depicted with carbon atoms numbered from 1 to 6. The structure is hexagonal with a ring of oxygen at the top right connecting Carbon 1 (C1) and Carbon 5 (C5). The following groups are attached on each carbon:
- Carbon 1 (anomeric carbon): — OH
- Carbon 2: — OH
- Carbon 3: — OH
- Carbon 4: — OH
- Carbon 5: — CH2OH
- Carbon 6: — OH (pointing upwards)
Each carbon atom is part of the ring and contributes to the hexagonal arrangement.
**Options:**
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question Completion Status: O D. ketohexose QUESTION 40 Classify the following monosaccharide as an aldopentose, ketopentose, aldohexose, or ketohexose H *********** HO-C-H HO-C-H H-C-OH CH₂OH A. aldopentose B. ketopentose O C. aldohexose O D. ketohexose QUESTION 41 How many grams of glucose are needed to prepare 400. mL of a 0.50% (m/v) glucose solution?arrow_forward3. A(n) is a molecule that is synthesized in one part of the body and has an effect in a different part. A) fatty acid B) enzyme C) hormone D) vitamin 4. DNA is a double-stranded nucleic acid that exists as a double helix. Which is responsible for holding the double helix of DNA together? A) Phosphodiester bonds between complementary base pairs on each strand B) B-N-glycosidic linkages between the sugar-phosphate backbone of each strand C) Disulfide bonds between the cysteine residues on each strand D) Hydrogen bonding between complementary bases on each strand 5. Which type of inhibitor is most likely to bind somewhere other than an enzyme's active site? A) competitive B) lock and key C) noncompetitive D) substrate 6. The compound shown below is best classified as what type of lipid? HO, A) Triacylglycerol B) Soap C) Fatty acid D) Waxarrow_forwardTrue or False 1. Mutarotation affects the reducing property of carbohydrates. 2. Anthrone test can be use to test for the helical configuration of a polysaccharide. 3. Upon treatment with phenylhydrazine reagent & hydrolysis, maltose gives glucuronic acid and glucosazone.arrow_forward
- Question 17 of 45 Plants store excess glucose as starch which is composed of amylose and amylopectin. Identify the characteristics of amylopectin. A) A straight chain polysaccharide containing only straight chain a-1-4 linkages of glucose residues. B) A polysaccharide containing a-1-4 linkages of glucose units and branching due to a-1-6 linkages of glucose residues C) A straight chain polysaccharide with a-1-4 linkages of glucose and galactose residues D) A branching polysaccharide containing a-1-4 linkages of glucose and galactose residues E) A branching polysaccharide containing a-1-4 linkages and a-1-6 linkages of glucose and galactose residues Submit +arrow_forwardHW 11 #19arrow_forwardHW11 #22arrow_forward
- *22) Draw the Fischer projection and Hayworth formula for D-galactose - the C4 epimer of D- glucose. (Okay to skip this for discussion with molecular models in lab.) Fischer projection of D-galactose Hayworth formula of a-D-galactose Reactions and Disaccharides 23) Aldehydes are oxidized to: 24) Open-chain aldoses can be oxidized, so they are called 'reducing sugars'. When D-glucose is oxidized, what is the carboxylic acid formed? 25) Can the hemiacetal be oxidized? 25) Can a ketose be oxidized? CHM60 Lecture Worksheet: Carbohydrates J 5 2arrow_forward1) What is epimerization? A) It involves changing the configuration of a carbon B) It involves oxidation of an aldose. C) It involves lengthening the chain of an aldose. D) It involves reduction of an aldose. E) none of the above 2) Which of the following monomer: polymer pairings is mismatched? a. Amino acids: proteins b. Amino acids: peptides c. Monosaccharides: polysaccharides d. Nucleotides: DNA e. They are all correctly matched 3) How do the a and ẞ anomer of a sugar differ? a. By the configuration of the acetal carbon in the ring form b. c. By whether a ketone or aldehyde is present in the straight chained form By the presence/absence of a 2' OH d. By whether the OH on the last chiral center is pointed right or left in the Fischer projection of the straight chained form 4) A salt bridge can occur as part of the apply) a. Primary structure b. Secondary structure of a protein (select all that c. Tertiary structure d. Quaternary structuré 5) True or false: A protein that has been…arrow_forwardWhich of the following will produce both glucose and galactose when it is hydrolyzed? a) Sucrose b) maltose c) lactose d) amylosearrow_forward
- Raffinose is a trisaccharide found in whole grains. What is the correct description of the glycosidic linkage(s) in raffinose?arrow_forwardPlease complete the following question. There is no need to provide an explaination. 7arrow_forward346 Laboratory Manual for General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Q2 From the results in Part B, which carbohydrates are ketoses? Q3 From the results in Part C, which carbohydrates give a positive fermentation test? Q4 From the results in Part D, which carbohydrates give a blue-black color in the iodine test? isubs vol Identifying an Unknown Carbohydrate Unknown No. Results with Unknown Carbohydrates Present Benedict's (A) Seliwanoff's (B) Fermentation (C) Iodine (D) What carbohydrate(s) is/are in your unknown? bot O Questions and Problems Q5 What carbohydrate(s) would give the following test results? a. Produces a reddish-orange solid with Benedict's reagent and a red color with Seliwanoff's reagent in 1 minutearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic And Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305081079
Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning