
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please solve question b) and c)
* The seized tusks came for elephant #8.
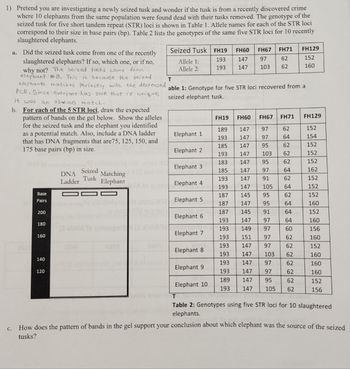
Transcribed Image Text:1) You are investigating a newly seized tusk to determine if it is from a crime scene where 10 elephants from the same population were found dead with their tusks removed. The genotype of the seized tusk for five short tandem repeat (STR) loci is shown in Table 1. Allele names for each of the STR loci correspond to their size in base pairs (bp). Table 2 lists the genotypes of the same five STR loci for 10 recently slaughtered elephants.
**a.** Did the seized tusk come from one of the recently slaughtered elephants? If so, which one, or if not, why not?
The seized tusk came from elephant #8. This is because the seized elephant’s matches perfectly with the deceased PCR. Since everyone has DNA that is unique, it was an obvious match.
**b.** For each of the 5 STR loci, draw the expected pattern of bands on the gel below. Show the alleles for the seized tusk and the elephant you identified as a potential match. Also, include a DNA ladder with DNA fragments that are 75, 125, 150, and 175 base pairs (bp) in size.
(Graph Explanation: A diagram showing a DNA ladder with base pairs marked at 75, 125, 150, and 175. Alongside, bands for the seized tusk and matching elephant are drawn to illustrate the alleles.)
**c.** How does the pattern of bands in the gel support your conclusion about which elephant was the source of the seized tusks?
The pattern of bands in the gel supports that the seized tusk came from elephant #8 because the band sizes (alleles) perfectly match between the seized tusk and elephant #8 at all five loci.
---
**Table 1:** Genotype for five STR loci recovered from a seized elephant tusk.
- **Allele 1:** 193, 147, 97, 62, 152
- **Allele 2:** 193, 147, 103, 62, 160
**Table 2:** Genotypes using five STR loci for 10 slaughtered elephants.
- **Elephant 1:** 189, 147, 97, 62, 152; 193, 147, 97, 64, 154
- **Elephant 2:** 185, 147, 95, 62, 152
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What do you think about the hypothesis that language evolved as a way for early hominins to communicate about stone-tool manufacturing? What other hypothesis could you come up with as to why language evolved in our Hominini tribe?arrow_forwardFind a representative fish from types A-C. Give the species name of the fish, its family, and what kind of tail it has. Please answer all parts to this questionarrow_forwardAccording to "The Life and Death of a Neanderthal (Shanidar 1)”, what were some of Nandy’s physical injuries? A.Loss of both legs and bony growths in both ears causing partial deafness. B.Loss of right forearm, crushed left eye socket, injuries to leg and knees, bony growths in both ears causing partial deafness. C.Loss of both arms and bony growths in both ears causing partial deafness. D.Loss of right forearm, crushed left foot, injuries to ankles and elbows, bony growths in both ears causing partial deafness.arrow_forward
- Orrorin tugenesis was bipedal because it left footprints that showed it had an arch to its foot like modern humans. True or Falsearrow_forwardWhat is the significance of bipedalism for hominins? What benefits does bipedalism offer and what environmental changes made bipedalism an important adaptation for hominin species?arrow_forwardAccording to "The Complex Evolution of Homo sapiens", there is NO archaeological evidence to suggest that Homo sapiens left Africa any sooner than genetic evidence suggests. A. True B. Falsearrow_forward
- According to "The Life and Death of a Neanderthal (Shanidar 1)”, what finally killed Nandy? A.He lost his leg in battle B.A cave-in C.A spear to the back D.A tooth infectionarrow_forwardAccording to "Homo erectus – The First Humans”, what stone tool is believed to be developed by Homo erectus? A.Oldowan Chopper B.Levallois Flake C.Acheulean Hand Axe D.Levallois Fishing Rodarrow_forwardWhy is it interesting that Homo luzonensis was found on an island? A. The islands only formed after Homo luzonensis became extinct, so Neanderthals must have put them on the island B. The islands were a few miles apart, and Homo luzonensis would have needed to either float by grabbing on a tree or make a raft C. The islands were a few miles apart, and Homo luzonensis clearly had to learn how to fly to get to them D. The islands were volcanoes when Homo luzonensis was alive, so it's unexpected that they were therearrow_forward
- Taphonomic analysis of Neanderthal remains has found that they have a pattern of trauma similar to that seen in modern-day rodeo riders. This was interpreted to mean that Neanderthals: A. Had projectile weapons and could hunt large game from a distance. B. Were riding large animals like horses and reindeer. C. Had hostile interactions with modern humans migrating into the area. D. Were a war-like species that fought amongst themselves a lot. E. Had to hunt large game at close range.arrow_forwardPlease answer the questions and write paragraph. 3: What piece of information did the researchers use to suggest that Homo erectus did not have much body hair? 4: Where is Dmanisi? Why is it important? 5: Name three things about Homo erectus that separate them from the earlier hominins, including Homo habilis?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education