
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
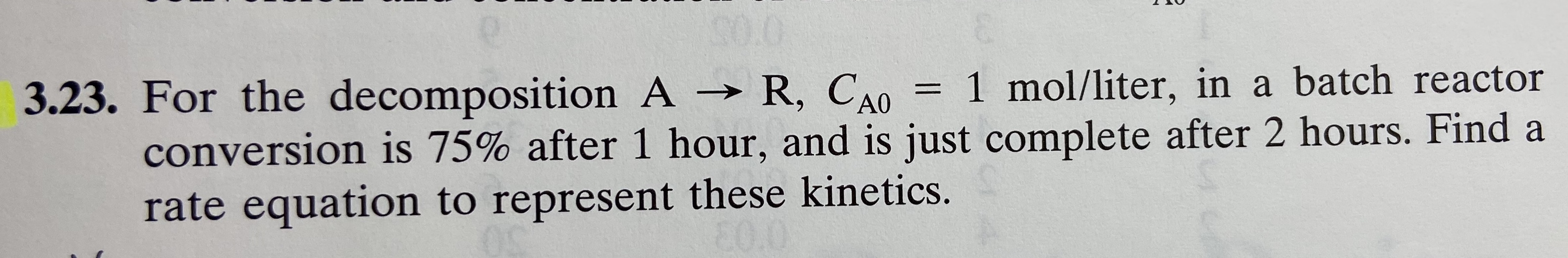
Transcribed Image Text:= 1 mol/liter, in a batch reactor
3.23. For the decomposition A R, CAO
conversion is 75% after 1 hour, and is just complete after 2 hours. Find a
rate equation to represent these kinetics.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You are in a research & development team responsible for generating preliminary data for the following gas-phase reaction: CO₂(g)+ 4H₂ (g) → 2 H₂O (g) + CH.(g) The reaction occurs over a catalyst at a reactor pressure of 1 atm and 500 C and goes essentially to completion. Use the following heat capacities data for your calculation: CO₂ (g): H₂ (g): H₂O (g): CH₁ (g): Cp=0.0451 kJ/mol C Cp = 0.0291 kJ/mol C Cp = 0.0358 kJ/mol C Cp=0.0487 kJ/mol C a) Calculate the standard heat of reaction (kJ/mol). (-165.01 kJ/mol) b) If the gases enter and leave the reactor at 1 atm and 500 C, what is the heat of reaction at 500 C (i.e. Ê, at 500 C) in kJ/mol. Assume the reactants are fed in stoichiometric amounts. (-184.63 kJ/mol)arrow_forwardGive answer all questions with explanationarrow_forwardThe following elementary gas-phase reaction has a rate constant of 20 L⁄mol min at 350 K. A + B → C The reaction is carried out in an isothermal, isobaric PFR at 350 K and 2 atm. The feed is a 30:60:10 mixture of A:B:inert. The feed flow rate of A is 5 mol/min. (a) Determine the PFR volume required to achieve a conversion of 90%. (b) Determine the conversion that could be achieved if the PFR volume were half of the volume calculated in part (a). Give your answer correct to 3 s.f. (c) Present your answers to parts (a) and (b) on a single Levenspiel Plot.arrow_forward
- 1. A house needs 200,000 Btu per day so that its temperature remanins at 68oF. How much CaCl26H2O(s) needs to be used to save enough energy for one day use? The process contains the heating of CaCl26H2O(s) from 68oF to 86oF and the reaction CaCl26H2O(s) = CaCl22H2O(s) + 4H2O(g). The water from the dehydration evaporates during the process. CaCl26H2O(s): ΔHof=-2607.89kJ/gmol, Cp=1.34J/g(oC) CaCl22H2O(s): ΔHof=-1402.90kJ/gmol, Cp=0.97J/g(oC)arrow_forward* The standard reaction enthalpy for the hydrogenation of propene is -124 KJ/mole. The standard reaction enthalpy for the combustion of propane is -2220 KJ/mole. What is the standard enthalpy of combustion (in KJ/mole) of propene given that the enthalpy of formation for liquid water is -285.5 KJ/mole? NOTE: Express answer in the NEAREST WHOLE NUMBER.arrow_forwardDirect dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene to styrene is carried out in the vapor phase with steam over a catalyst consisting primarily of iron oxide. The reaction is endothermic, and can be accomplished either adiabatically or isothermally. Both methods are used in practice. The major reaction is the reversible, endothermic conversion of ethylbenzene to styrene and hydrogen: C6H3CH₂CH CoHsCHCH₂ + H₂ AH= 124.9 kJ/mol Competing thermal reactions degrade ethylbenzene to benzene C6H3CH₂CH3C6H6+ C₂H4 AH 101.8 kJ/mol Styrene also reacts catalytically to toluene: CH3CH₂CH3 + H2 CH3CH3 + CH4 AH=64.5 kJ/mol The reactions take place at 620°C. The costs are as shown in Table 1. The production rate of styrene is 200 mol/h. Chemical name Formula Cost (S/kmol) Ethylbenzene C6H5CH₂CH3 57.1 Styrene C.HSCHCH₂ 75.9 Benzene C6H6 32.8 Toluene C6H5CH3 25.8 Hydrogen H₂ 1.2 (as fuel) Methane CH4 4.0 (as fuel) Ethylene C₂H4 6.7 (as fuel) Correlation for the product selectivity and distribution are given as…arrow_forward
- Product B is produced in a batch reactor according to the elemental reversible reaction (A⇋B) in liquid phase. The reactor volume is 10 L and the reaction temperature is 60°C. The initial concentration of reagent A is 3 lbmol/L, the rate constant for the forward reaction is k1=6.0 h-1, and the rate constant for the reverse reaction is k2=0.53h-1. Determine: (a) Plot the concentration of each species as a function of reaction time(b) Plot the conversion as a function of reaction timearrow_forwardPlease only solve part Darrow_forwardInto a combustion reactor, hexane at 55 mol and 25% excess dry air are fed. The fractional conversion of hexane is 85%. Assume that air is 21 mol% oxygen and 79 mol% nitrogen. The governing equation for the combustion reaction is: 2 C6H14 + 19 O2 → 12 CO2 + 14 H2O a. Draw a complete flowchart of the process. Clearly state any assumptions. b. Perform a degree-of-freedom analysis (atomic species DOF). c. What is the mole fraction of carbon dioxide in the flue gas on a dry basis? PLEASE Solve using ATOMIC SPECIES, thank youarrow_forward
- 4arrow_forwardProblem 2 What is the volume of a plug flow reactor with an elementary gas-phase reaction A⇒ 3R and a desired conversion of 85%? The feed consists of 50% A and 50% inerts at 190 °C and 4 atm and enters at 0.4 mol/s. The reaction rate constant is 0.01 s¹ at 190°C. Assume no drop in pressure and isothermal operation and ideal gas laws.arrow_forward4) (10 points) For the reaction A+B>2C Given the following data, what is the heat of reaction (AHR) at 400°F? Cpa = 35 (BTU/lb mol °F); C8 = 15 (BTU6 mol °F); C,c = 45 (BTU/lb mol °F) AHR (100°F) = -66,000 (BTU/lb mol A); %3Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The