
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
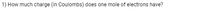
Transcribed Image Text:1) How much charge (in Coulombs) does one mole of electrons have?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. Two infinite sheets of equal and opposite charge are placed facing each other with a distance of 1.50 m separating them. The positive sheet is on the left and the negative sheet is on the right. If a lone point charge of -5.00 µC with a mass of 3.15 x 10-7 kg is at the midpoint between the plates and is released from rest, it reaches the positive sheet with a speed of 1200 m/s. a) Through what electric potential difference did the point charge move?arrow_forward3. An isolated system consists of two metal spheres, with sphere 2 having twice the radius of sphere 1. Both spheres are initially charged as shown in the initial figure. The two spheres are then brought into contact with each other so that charge, in the form of electrons, is transferred between them. The spheres are then separated as shown in the final figure, where they have unknown charges, q and q2. Since sphere 2 has twice the radius, it will have twice the amount of charge than sphere 1 in the final state. Find q, q and the number of electrons transferred between the spheres. Hint: The net charge of the two-sphere system is conserved, since it is an isolated system. initial electron transfer between spheres final 91 = +12.0 μC 9₁ = ? q2 = -3.00 μC 9₂ = ?arrow_forward1. Common static electricity involves charges ranging from nanocoulombs to microcoulombs. (a) How many electrons are needed to form a charge of −9.10 nC? electrons (b) How many electrons must be removed from a neutral object to leave a net charge of 0.520 µC? electrons 2. What net charge would you place on a 412 g piece of sulfur if you put an extra electron on 1 in 1012 of its atoms? (Sulfur has an atomic mass of 32.1.) 4. What is the repulsive force between two pith balls that are 10.0 cm apart and have equal charges of −39.0 nC?-------N 6.How far apart (in mm) must two point charges of 65.0 nC (typical of static electricity) be to have a force of 5.50 N between them? 7. a.What is the direction of this force (away from or toward the +6 µC charge)? away from the +6 µC chargetoward the +6 µC charge ---------mm A test charge of +9 µC is placed halfway between a charge of +6 µC and another of +7 µC separated by 17 cm. (b) What is the magnitude of the force (in N)…arrow_forward
- 3. Two small aluminium spheres weighing 10 g each are suspended by 10-cm-long silk threads from two hooks separated 10 cm apart. When the spheres are uncharged, the silk threads are vertical due to the gravitational pull of the earth (the effect of gravity between the two spheres is negligible). A fraction of the electrons from each sphere is then removed, leaving behind a net positive electric charge on each sphere. Once the spheres are charged, they move away from each other causing the thread to hang at 45 degrees from vertical. a) What is the net positive charge on each sphere? Hint: The horizontal and vertical forces acting on each sphere must be equal for the net force to be along a 45 degree angle. b) Given that the atomic mass of Aluminium is 27 and the atomic number is 13, what percentage of total electrons of the aluminium spheres need to be taken away to achieve this scenario?arrow_forward4.) Figure Q.2 (b) shows a cylindrical structure with length of 50 m. The inner and the outer surface are separated by free space and located at r = a and r = b respectively. The inner and outer surface of the structure contain a total charge of +1pC and -1pC, respectively. An infinitely long line charge with line charge density of +1pC/m is introduced along the axis of the structure. Given that a = 1 mm and b = 2 mm. +pa C/m? -Рь С/m? Figure Q.2(b) i. Calculate +pa and -pp at radius a and b respectively ii. Find D and E in all regions iii. Sketch graph |D| versus rarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON