
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:1) Consider the capacitor circuit as shown in the figure below. They are connected an EMF of 15 V.
(a) Find the equivalent capacitors for the circuit shown below
(b) Find the charge in the capacitors C4
(c) Find the charge in the capacitors C2
(d) Find the charge in the capacitors C6
(e) Find the energy stored in C1
(f) Find the energy stored in C5
(g) Find the total energy stored in the circuits.
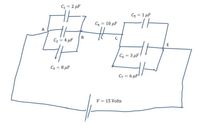
Transcribed Image Text:C = 2 µF
C5 = 1 µF
C4 = 10 µF
%3D
A
C2 = 4 µF
E
C6 = 3 µF
C3 = 8 µF
C7 = 6 µF
V = 15 Volts
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Inductors are fundamental components in electronics and electrical circuits. They are passive devices that store energy in the form of a magnetic field when crossed by an electric current. Inductors consist of a wire wound around a core, often made of iron or another ferromagnetic material. The storage of magnetic energy in inductors is expressed in terms of inductance, measured in henries (H). What is the value of inductive reactance (XL) in ΩΩ, exhibited by the inductor in the circuit below?arrow_forwardFind the voltage across and the charge stored in capacitor C1.arrow_forwardDescribe in words how the charges behave on capacitors which are in a parallel circuit. How do the individual capacitor charges compare to the charge of the equivalent capacitor?arrow_forward
- Switch S in in the figure is closed at time t = 0, to begin charging an initially uncharged capacitor of capacitance C= 17.9 µF through a resistor of resistance R = 22.7 Q. At what time is the potential across the capacitor equal to that across the resistor? Number i Units S R Carrow_forwardThe illustration shows four capacitors that are connected together in a so-called capacitor bridge. Initially, the capacitors are uncharged. Which relationship must hold between the four capacitances so that the voltage between points c and d remains zero when a voltage U is applied between points a and b?arrow_forwardIn the figure ɛ = inductor is ideal. If the switch is closed for a long time, what is the current through the inductor. Give your answer in A. 10.0 V, R, = 4.00 N, and R2 = 1.00 N. The %3D %3Darrow_forward
- Picture shown three capacitors with capacitances C1=6.00μF,C2=3.00μF,C3=5.00μF . The capacitor network is connected to an applied potential Vab. After the charges on the capacitors have reached their final values, the charge Q2 on the second capacitor is 40.0 μC. Part A What is the charge Q1 on capacitor C1? Part B What is the charge on capacitor C3? Express your answer in microcoulombs to three significant figures. Part C What is the applied voltage, Vab? Express your answer in volts to three significant figures.arrow_forwardThree capacitors, with capacitances of C1 = 2.0 μF, C2 = 3.0 μF , and C3 = 6.0 μF, respectively, are connected in parallel. A 500-V potential difference is applied across the combination. Determine the voltage across each capacitor and the charge on each capacitor.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is TRUE? O a) The major reason for using electrolytic capacitors is that they have a very low a) capacitance but can handle very low voltages. O b) Increasing the distance between the plates of a capacitor would yield a higher capacitance. OdA capacitor is rated according to its maximum allowable voltage and c) capacitance value. d) Electrolytic capacitors are non-polarized.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,