
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
a. What is the heat flux, q"1 [in W/m2], at the left-hand side of layer B? Express your answer as a negative number if the heat flux goes to the left, and as a positive number if the heat flux goes to the right.
b.What is the heat flux, q"2 ( in W/m2) at the right-hand side of layer B? Express your answer as a negative number if the heat flux goes to the left, and as a positive number if the heat flux goes to the right.
c. What is the temperature, T1, on the left-hand side of layer B, in Celsius?
d. What is the temperature, T2, on the right-hand side of layer B, in Celsius?
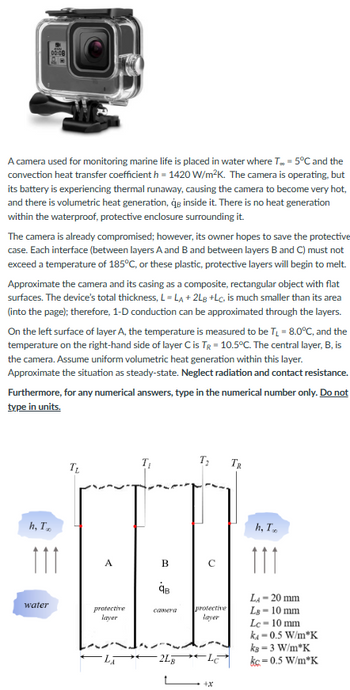
Transcribed Image Text:A camera used for monitoring marine life is placed in water where T.. -5°C and the
convection heat transfer coefficient h=1420 W/m²K. The camera is operating, but
its battery is experiencing thermal runaway, causing the camera to become very hot,
and there is volumetric heat generation, qe inside it. There is no heat generation
within the waterproof, protective enclosure surrounding it.
00:08
The camera is already compromised; however, its owner hopes to save the protective
case. Each interface (between layers A and B and between layers B and C) must not
exceed a temperature of 185°C, or these plastic, protective layers will begin to melt.
Approximate the camera and its casing as a composite, rectangular object with flat
surfaces. The device's total thickness, L=LA + 2LB +Lc, is much smaller than its area
(into the page); therefore, 1-D conduction can be approximated through the layers.
On the left surface of layer A, the temperature is measured to be T₁ = 8.0°C, and the
temperature on the right-hand side of layer C is TR-10.5°C. The central layer, B, is
the camera. Assume uniform volumetric heat generation within this layer.
Approximate the situation as steady-state. Neglect radiation and contact resistance.
Furthermore, for any numerical answers, type in the numerical number only. Do not
type in units.
h, T
111
water
T₂
A
protective
layer
B
qв
camera
2Lg
T₂
с
protective
layer
*
TR
h, T
111
LA - 20 mm
LB-10 mm
Lc-10 mm
ka=0.5 W/m*K
kB = 3 W/m*K
kc-0.5 W/m*K
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
“Since you have posted a question with multiple sub-parts, we will solve first three sub-parts for you. To get remaining sub-part solved please repost the complete question and mention the sub-parts to be solved” - according to Bartleby QnA guidelines.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
What is the temperature, T2, on the right-hand side of layer B, in Celsius and the uniform volumetric heat generation, q̇B [W/m3], within layer B?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
What is the temperature, T2, on the right-hand side of layer B, in Celsius and the uniform volumetric heat generation, q̇B [W/m3], within layer B?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are designing a 3m x 3m floor with radiant heating. The floor has 12 parallel pex pipes (k = 40 W/mK) of L = 3m, OD = 25mm and ID = 20mm. Hot water (TInfintiy 1 = 90oC, h = 200 W/m2K) runs through the pipes continuously. The surface below the pipes is perfectly insulated. Above the pipes, there is a 3mm layer of bonding material (? = 12 W/mK) and a 9mm layer of tile (k = 2 W/mK). Above the tile, there is air (TInfinity 2 = 25oC, h = 20 W/m2K). Properties of Air: k = 0.025 W/mK, Pr = 0.72, v = 1.847 x 10−5, u = 16.84 x 10−6, p = 1.2 kg/m3, B = 1/Tf (ideal gas), Hint: Assume that the “layer” of pipe starts at the center point (e.g. for conduction purposes, the pipe is OD divided by 2 thick). For convection, consider the entire pipe surface. a) What is the total heat rate entering the room above the floor? b) What is the temperature of the top of the tile?arrow_forwardA solar collector and storage tank, shown in Figure (a) below, is to be optimized to achieve minimum first cost. During the day the temperature of water in the storage vessel is elevated from 25 °C (the minimum useful temperature) to tmax, as shown in Figure (b). The collector receives 260 W/m² of solar energy, but there is heat loss from the collector to ambient air by convection. The convection coefficient is 2 W/(m²*K), and the average temperature difference during the 10-hour day is (25 + tmax)/2 minus the ambient temperature of 10 °C. The energy above the minimum useful temperature of 25 °C that is to be stored in the vessel during the day is 200,000 kJ. The density of water is 1000 kg/m³, and its specific heat is 4.19 kJ/(kg*K). The cost of the solar collector in dollars is 20A, where A is the area in square meters, and the cost of the storage vessel in dollars is 101.5V, where V is the volume in cubic meters. Storage tank Collector (a) Temperature, °C tmax conforte 25°C, lowest…arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY