
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Two bowling balls are at rest on top of a uniform wooden
plank with their centers of mass located as in Figure P8.9. The
plank has a mass of 5.00 kg and is 1.00 m long. Find the horizontal
distance from the left end of the plank to the center of
mass of the plank–bowling balls system.
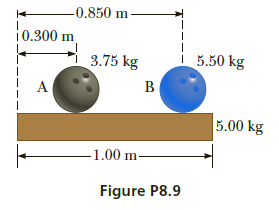
Transcribed Image Text:-0.850 m
10.300 m
5.50 kg
3.75 kg
A
5.00 kg
-1.00 m-
Figure P8.9
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Kathrine lets go of a cube of mass of m = 5 kilograms on her physics demo device she created. Her cube goes down a super smooth slide surface that has a height vertical distance of h=85 cm. At the end of the slide, her cube crashes into and sticks to the lower end of a vertical pole that has a mass M=10.5 kg and length 1-2.00m. Right after the crash, the pole pivots about a hinge point near its upper end through an angle (theta) before it stops for a moment. See the image given below to visualize Katherines system. You are tasked with Figuring out the following three things The speed of her cube just before it hits the pole The angular speed of the pole just after the crash The angle (theta) through which the pole pivots a. b. C. 0 Kathrine and her devicearrow_forwardConsider the following mass distribution where the x- and y-coordinates are given in meters: 5.0 kg at (0.0, 0.0) m, 2.5 kg at (0.0, 3.9) m, and 4.0 kg at (3.2, 0.0) m. Where should a fourth object of 9.4 kg be placed so that the center of gravity of the four-object arrangement will be at (0.0, 0.0) m? x = y =arrow_forwardConsider the following mass distribution where the x- and y-coordinates are given in meters: 5.0 kg at (0.0, 0.0) m, 2.7 kg at (0.0, 4.6) m, and 4.0 kg at (3.2, 0.0) m. Where should a fourth object of 7.8 kg be placed so that the center of gravity of the four-object arrangement will be at (0.0, 0.0) m? x = m y = marrow_forward
- Consider the following mass distribution where the x- and y-coordinates are given in meters: 5.0 kg at (0.0, 0.0) m, 3.4 kg at (0.0, 3.7) m, and 4.0 kg at (2.9, 0.0) m. Where should a fourth object of 8.6 kg be placed so that the center of gravity of the four-object arrangement will be at (0.0, 0.0) m? X = y = m Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardA 7 meter long stick is suspended from two strings. The stick has a mass of 17kg that is uniformily distributed. A 9kg dog is sitting 0.7m from the left end of the stick. Where is the center of mass? How do you know?arrow_forwardA uniform, 20-kg, 8.0-m-long, wooden plank that is parallel to level ground is supported by two pivots: one pivot is at the extreme left end of the plank, and the other pivot is 3.0 m inward from the extreme right end of the plank. A 80-kg construction worker, who is initally standing on the extreme left end of the plank, begins to walk to the right. How far from the right end of the plank will the worker be located when the plank begins to tip? 4.0 m 4.0 m 5.0 m a. 4.50 m O b.5.00 m O c. 4.25 m d. 5.25 m O e. 4.75 marrow_forward
- A wood plank has a length of 4.2 m and a mass of 14.3 kg. The plank is balanced between two saw horses. One saw horse is positioned directly under one end of the plank, and the other is located a distance d1 = 3.2 m away. A child with a mass of 29 kg walks along the plank, as if it were a balance beam. What is the furthest distance d2 (in meters) from the end of the plank that the child can walk before the plank tips and falls? NOTE: When the plank starts to tip, one of the forces becomes zero.arrow_forwardAmong the elderly population, a sideway fall is a most frequent cause of hip fracture. An old man of mass 65 kg and height 1.7m was sent to Prince of Wales Hospital due to sideway fall. He slipped and fell laterally down with a straight body. Before falling, his centre of mass was 0.9 m above ground. His centre of mass was on the ground at the end of the fall. The radius of gyration about the anterior-posterior axis at his centre of mass was 0.55 m. (a) Calculate the initial potential energy before his fall. (b) Assuming his potential energy would be converted to linear kinetic energy of his centre of mass and rotational kinetic energy about his centre of mass, calculate the impact velocity v of his centre of mas right before he hit the ground. C. M. 1.7m 0.9marrow_forwardConsider the following mass distribution where the x- and y-coordinates are given in meters: 5.0 kg at (0.0, 0.0) m, 2.9 kg at (0.0, 3.3) m, and 4.0 kg at (3.5, 0.0) m. Where should a fourth object of 9.4 kg be placed so that the center of gravity of the four-object arrangement will be at (0.0, 0.0) m? x = m y = marrow_forward
- A 550.0 g bird is flying horizontally at 2.50 m/s, not paying much attention, when it suddenly flies into a stationary vertical bar, hitting it 25.0 cm below the top. The bar is uniform, 0.700 m long, has a mass of 1.50 kg kg, and is hinged at its base. The collision stuns the bird so that it just drops to the ground afterward (but soon recovers to fly happily away). What is the angular velocity of the bar just after it is hit by the bird? Express your answer in radians per second. W1 = rad/sarrow_forwardConsider the following mass distribution where the x- and y-coordinates are given in meters: 5.0 kg at (0.0, 0.0) m, 3.4 kg at (0.0, 3.6) m, and 4.0 kg at (3.4, 0.0) m. Where should a fourth object of 7.2 kg be placed so that the center of gravity of the four-object arrangement will be at (0.0, 0.0) m? X = y = m Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardConsider the following distribution of objects: a 4.00-kg object with its center of gravity at (0, 0) m, a 5.20-kg object at (0, 3.00) m, and a 1.40-kg object at (2.00, 0) m. Where should a fourth object of mass 7.00 kg be placed so that the center of gravity of the four-object arrangement will be at (0, 0)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON