
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
1) A white bomb made of a composition of TNT and RDX with a mass of 1.2-kg moving along the x-axis is exploded at the origin into two pieces. The speed of the bomb before the explosion was 0.50 m/s. The mass of the pieces and the speed of the piece moving vertically are shown in the figure below:
a)What is the angle θ, (which is the angle made by the velocity of the second piece and x-axis)?
b) What is the speed of the second piece?
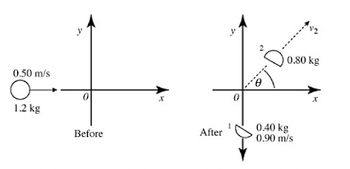
Transcribed Image Text:0.50 m/s
1.2 kg
y
Before
After
0.80 kg
0.40 kg
0.90 m/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A green toy car with 0.025-kg mass moves to the right at 0.30 m/s and has a head-on, elastic collision with a black 0.045-kg toy car which is at rest on a smooth, level surface. Which of the following are the correct magnitudes and directions of the velocities of the two toy cars after the collision? 0.025 kg toy car 0.045 kg toy car A) 0.09 m/s, left 0.21 m/s, right B) 0.10 m/s, right 0.30 m/s, right C) zero m/s 0.25 m/s, right D) 0.20 m/s, left 0.20 m/s, right E) 0.20 m/s, left zero m/sarrow_forward1) a) Mass m1 = 0.25 kg is moving with a velocity Vr = 10 m/s and collides with mass m2 = l kg whichis at rest. After the collision, the mass m1 moves in the opposite direction with a velocity v1' = -4 m/s. What is the velocity v2', of the mass m2 subsequent to the collision?b) What is the total kinetic energy prior to the collision? What is the total kinetic energy subsequent to the collision? How much heat was generated in the collision process?arrow_forwardTwo spheres, each of mass m, can slide freely on a frictionless, horizontal surface. Sphere A is moving at a speed v0 = 16 ft/s when it strikes sphere B which is at rest, and the impact causes sphere B to break into two pieces, each of mass m/2.a) Knowing that 0.7 s after the collision one piece reaches Point C and 1.17 s after the collision the other piece reaches Point D, determine the velocity of sphere A after the collision.b) Knowing that 0.7 s after the collision one piece reaches Point C and 1.17 s after the collision the other piece reaches Point D, determine the angle θ and the speeds of the two pieces after the collision.arrow_forward
- 1) A toy car having mass m = 1.35 kg collides inelastically with a toy train of mass M = 3.70 kg.Before the collision, the toy train is moving in the positive x-direction with a velocity of Vi = 2.10 m/s and the toy car is also moving in the positive x-direction with a velocity of vi = 4.70 m/s. Immediately after the collision, the toy car is observed moving in the positive x-direction with a velocity of 2.05 m/s. (a) Determine Vf, the final velocity of the toy train. ____m/s(b) Determine the change ΔKE in the total kinetic energy. Assume friction and the rotation of the wheels are not important so that they do not affect ΔKE. ____J Question 6.1b:2) A block with mass M = 6.10 kg is sliding in the positive x-direction at Vi = 8.90 m/s on a frictionless surface when it collides elastically in one dimension with a stationary block with mass m = 1.40 kg. Determine the velocities, Vf and Vf of the objects after the collision. Vf= ___m/s Vf=___m/sarrow_forward52. The Center of Mass of Sulfur Dioxide Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) consists of two oxygen atoms (each of mass 16 u, where u is defined in Problem 40) and a single sulfur atom (of mass 32 u). The center-to-center distance between the sulfur atom and either of the oxygen atoms is 0.143 nm, and the angle formed by the three atoms is 120°, as shown in Figure 9-20. Find the x and y coordinates of the center of mass of this molecule. Oxygen 0.143 nm y 120° Oxygen 0.143 nm Sulfur A FIGURE 9-20 Problem 52 Iarrow_forwardA ball has a mass of 10-Kg and is traveling to the right at 30 m/s. A second ball, which is suspended from a string and has a mass of 15-Kg, is traveling to the left at 12 m/s. The two balls experience an elastic head-on collision when the string is vertical. Determine:a) the speed of each ball after impactb) the height that the second ball will rise with respect to its lowest position (AFTER IMPACT)arrow_forward
- moving speeds of v₁ = 5.2 m/s m₂ = 2m₁. After the collision Two Particles are and V₂0 and mass mi Of 90° relative to its direction prior to elastic. The collision is is observed to be moving at an angle the Collision, Define a Suitable coordinate system and determine the final velocities (including direction) of each Partille, It also may be useful to remember that cos(20) = Cos²-sin².arrow_forwardFor a system of three particles moving along a line, an observer in a laboratory measures the following masses and velocities. What is the velocity of the CM of the system? Enter a positive value if the velocity of the CM of the system is in the +x direction and enter a negative value if the velocity of the CM of the system is in the -x direction. Mass (kg) Vx (m/s) 4.00 230 5.0 -120 2.0 +52 m/sarrow_forwardProblem B) An inelastic collision occurs between a particle of mass 1.5 kg moving with an initial velocity of v = (-2i – 1.33 + 0.7k) m/s and another particle of mass 0.8 kg that has an initial velocity of v = (5.6å + 0.53 + 4.3k) m/s. What is the final velocity of the particles in unit vector notation? %3Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON