
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A member is made of a material that has a specific weight of g = 6 kN>m3 and modulus of elasticity of 9 GPa. If it is in the form of a cone having the dimensions shown in Fig. a, determine how far its end is displaced due to gravity when it is suspended in the vertical position.
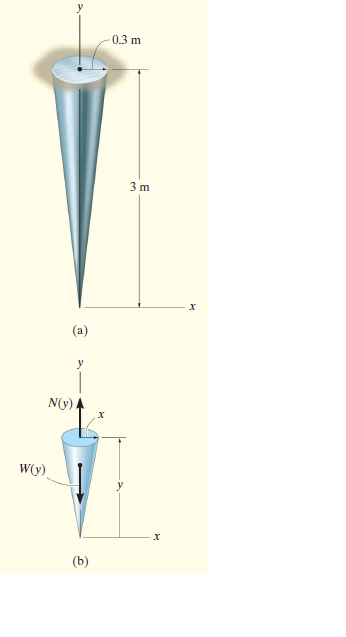
Transcribed Image Text:0.3 m
3 m
(a)
N(y)
W(y)
(b)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the structure shown below, determine the magnitude of the roller reaction force at support A in kN. Consider 0 = 35 degrees, and w = 3 kN. Ignore the weight of the structure. Draw the FBD before proceeding to set up the equations. A 3 m 0 2m -4 m W Barrow_forward1.21 need assistance thank youarrow_forwardA 14m bar of negligible weight rest in a horizontal position on the smooth planes as shown. Compute the distance x at which load T = 250 kN should be placed from point B to keep the bar horizontal.arrow_forward
- can you help answer this question please? thank you.arrow_forward-1 m 1m Draw a Free-Body Diagram of the bars AD and BC shown in the figure. Assume all 1m 500 N hinges to be smooth and neglect the weight of each bars. 1 m B.arrow_forwardA uniform edge load of w1 = 530 lb/in. and w2 = 320 lb/in. is applied to the polystyrene specimen. Ep = 597(103)psi and νp = 0.25. 1) Part A: If the specimen is originally square and has dimensions of a = 1 in ., b = 2 in., and a thickness of t = 0.35 in. , determine its new dimension a′ after the load is applied. 2) Part B: Determine its new dimension b′ after the load is applied. 3) Part C: Determine its new dimension t′ after the load is applied.arrow_forward
- The timber member has a cross-sectional area of 1703 mm2 and its modulus of elasticity is 13.2 GPa. Compute the change in the total length (in mm) of the member after the loads shown are applied if x = 1.84, y = 3.63, and z = 4.11. Round off the final answer in two decimal places.arrow_forwardDetermine the angle that will yield a maximum force uh member BC, along with magnitude and nature of this force. Note: use method of sections and show solution. Answer should be 45° & BCmax = 168 kNarrow_forwardQ) For the shown truss, determine the stiffness matrix of member 1 (1 to 3) and member 2 (2 to 3)? Let A = 50X10 m² and E-210 GPa for all elements. 50 KN 30 m - 3 20 m 100 KN 30 m 40 marrow_forward
- q1 The steel block shown in is subjected to a compressive force on all directions. Determine the change in length of Z-direction if the change in length of Y- direction is (-1.3mm). E for steel =210*10° N/mm? and u=0.28). 20cm 10cm F Scm Farrow_forwardThe pyramidal truss section BCDEF is symmetric about the vertical x-z plane as shown. Cables AE, AF, and AB support a 3.3-kN load. Determine the force in member BE. The force is positive if in tension, negative if in compression. 220 mm 220 mm 270 mm 270 mm 350 mm Answer: BE= i 290 с 290 mum 2.1kn kNarrow_forwardIn the loaded truss shown :- AB=BC=CD=DE=2.8m, BF=CG=GI=DH=HJ=EK/2=4.2m. If the loading P=3.5kN, Calculate force in HK.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY