
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
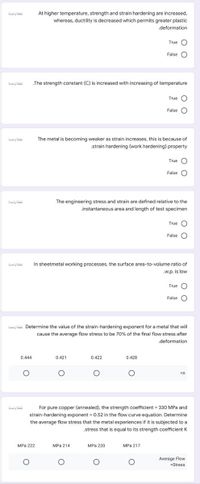
Transcribed Image Text:At higher temperature, strength and strain hardening are increased,
whereas, ductility is decreased which permits greater plastic
.deformation
True O
False O
.The strength constant (C) is increased with increasing of temperature
True O
False O
The metal is becoming weaker as strain increases, this is because of
.strain hardening (work hardening) property
نقطة واحدة
True O
False O
The engineering stress and strain are defined relative to the
.instantaneous area and length of test specimen
True O
False
aaly ihi
In sheetmetal working processes, the surface area-to-volume ratio of
.w.p. is low
True O
False
ialy ihii Determine the value of the strain-hardening exponent for a metal that will
cause the average flow stress to be 70% of the final flow stress after
.deformation
0.444
0.421
0.422
0.428
aals i
For pure copper (annealed), the strength coefficient = 330 MPa and
strain-hardening exponent = 0.52 in the flow curve equation. Determine
the average flow stress that the metal experiences if it is subjected to a
stress that is equal to its strength coefficient K
MPа 222
MPa 214
MPa 220
MPa 217
Average Flow
=Stress
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the tensile stress-strain diagram in the figure below labeled 1 and 2.arrow_forwardWhich is the correct definition of elastic deformation? The behavior of a material when its size changes by the addition of heat. The behavior describing a material's shape change under load that is self-reversing after the force is removed, so that the material returns to its original shape. The behavior describing a material that deforms when subjected to stress and does not return to its original shape when the stress is removed resulting in permanent deformation. Deformation caused by cleavage, where the material is actually pulled apart across atomic planes within the crystals or along the grain boundaries.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 You are working on a design team at a small orthopaedic firm. You have been asked to select a cobalt- chrome-molybdenum (CoCr) material that will not experience plastic deformation under a specific mechanical test, as follows... A tensile stress is applied along the long axis of a solid cylindrical rod that has a diameter of 10 mm. An applied load of some magnitude F produces a 7x10-³ mm change in diameter (see figure below, original shape is blue, elongated shape is unshaded). Q1E: Of those two materials (F75 CoCr alloy (as cast) and F90 CoCr alloy (hot forged)), which materials would you select to assure that the deformation is entirely elastic (No yield!)?arrow_forward
- What is the effect of strain hardening on the material?arrow_forwardHow does the resilience of this material compare to its toughness?arrow_forwardYou are given three metal test samples, with the same chemical composition and differing grain sizes: A: 5.0, B: 10.0 and C: 20.0 microns. Samples A and B have been tested and have yield stresses of 142.4 MPa and 135.8 MPa (all numbers are rounded off to the 1st decimal point). Based on this information, which of the following values do you think will be the closest to the yield stress of Sample C? In calculating the answer, use the Hall-Petch relation between yield stress of a metal o vield and the grain size of the metal d, which is Oyield = 00 + kd¬1/2 where k and og are constants. (This question has only one correct answer) а. 100.6 MPa b. 131.1 MPa С. 152.4 MPa O d. 115.8 MPa е. 128.1 MPaarrow_forward
- why use yield strength not tensile strength? You are drawing wire which you want the wire to elongate pernamently, and not return back to original shape .arrow_forwardclearly explain the terms linear strain and shear strain,what do they measure,how are they different ?use diagrams to explain the answerarrow_forwardMake sure you do the sketcharrow_forward
- Answer the following questions based on the given information in the table and further calculation (if needed for any missing parameter, e.g. strain at yield point). Assume all metals started with the same shape and size before the tensile tests occurred. Material A B C D E Yield Strength (MPa) 105 600 430 355 The material that experienced the greatest percent reduction in area is material The hardest material is material The hardest material has Tensile Strength (MPa) The material that experienced the greatest percent reduction in area has 135 850 The material that experienced the largest change in shape before plastic deformation occurred is material The stiffest material is material The stiffest material has 535 365 Fracture before yielding The material that experienced the largest change in shape before plastic deformation occurred has Strain at Fracture [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ] [Choose ] 0.45 0.15 0.20 0.25 Fracture Strength (MPa)…arrow_forwardNeed help on this Qarrow_forwardWhat are the experimental techniques used to measure the strain?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY