
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
1. Write the skeletal structures of propanal, acetone and cyclohexanone. What is the major intermolecular force (IMF) found in them? Based on their major intermolecular force and molecular weight, what can you predict on their solubility in water?
| Chemical Name | Skeletal Structures | Major IMF | Solubility in water |
| Propanal |
|
||
| Acetone |
|
||
| Cyclohexanone |
|
2. What is the purpose of Tollens’ test (Part B)? What is the evidence of a positive result?
3. What is the purpose of oxidation test (Part C)? What is the evidence of a positive result?

Transcribed Image Text:OBJECTIVES:
In this experiment, we will do a series of chemical reactions designed to characterize aldehydes and ketones.
You will be able to determine if a reaction has occurred by several means, including color changes and
chemical odors.
REAGENTS AND CHEMICALS:
Chromic acid solution
• Tollens' Reagent
.
Concentrated sulfuric acid (Be careful!)
• Benedict's Reagent
• Acetone
• Propanal
.
Cyclohexanone
PROCEDURE:
A. Benedict's Test for Aldehyde
Benedict's Test is often used to test for the presence of glucose in urine. It identifies aldehyde functional
group. For this part of the experiment, use the freshly prepared Benedict's reagent, add about 3 mL to three
very clean test tubes. To each of these tubes, containing the Benedict's reagent, add one of the following:
• Tube 1 : 2 drops of propanal
•
Tube 2:5 drops of acetone
• Tube 3: 10 drops of cyclohexanone
Place test tube in a boiling water bath and record the color development in 3-5 minutes, and note the results
in Table 1. The solution containing the glucose may take 10-15 minutes to react.
B. Tollens' Test (Silver mirror test) for Aldehydes
This test is based on the ability of an aldehyde (which is easily oxidized) to reduce silver ions in solution,
forming either a black deposit of free silver or a silver mirror within the test tube. The aldehyde group is
oxidized to an carboxylic acid during this reaction. Tollens' reagent is made by reacting silver nitrate solution
with diluted ammonium hydroxide. Rinse all glass equipment with distilled water before use.
Using the freshly prepared Tollens' Reagent, add about 3 mL to three very clean test tubes. To each of these
tubes, containing the Tollens' Reagent, add one of the following:
• Tube 1 : 2 drops of propanal
●
Tube 2: 2 drops of acetone
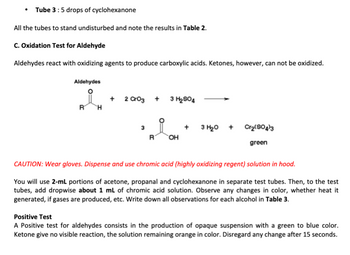
Transcribed Image Text:• Tube 3: 5 drops of cyclohexanone
All the tubes to stand undisturbed and note the results in Table 2.
C. Oxidation Test for Aldehyde
Aldehydes react with oxidizing agents to produce carboxylic acids. Ketones, however, can not be oxidized.
Aldehydes
R H
+ 2003 + 3 H₂SO4
R
OH
3 H₂0 +
Cr₂(SO4)3
green
CAUTION: Wear gloves. Dispense and use chromic acid (highly oxidizing regent) solution in hood.
You will use 2-mL portions of acetone, propanal and cyclohexanone in separate test tubes. Then, to the test
tubes, add dropwise about 1 mL of chromic acid solution. Observe any changes in color, whether heat it
generated, if gases are produced, etc. Write down all observations for each alcohol in Table 3.
Positive Test
A Positive test for aldehydes consists in the production of opaque suspension with a green to blue color.
Ketone give no visible reaction, the solution remaining orange in color. Disregard any change after 15 seconds.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
#1:
Propanal is an aldehyde(R-CHO) with 3 C atoms.
Acetone is a ketone(RCOR) with 3 C atoms.
Cyclohexanone is also a ketone(RCOR) with 6 C atoms.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following statements is FALSE about phenol? Select one: O A. It changes the colour of acidified potassium dichromate from orange to green. B. It is a stronger acid than ethanol, but a weaker acid compared to ethanoic acid. O C. It gives a purple solution with iron (II) chloride. D. It yields white precipitate with bromine water.arrow_forwardWrite the reactions as structural diagrams to represent the reaction that takes place between each alcohol and sodium as well as the oxidizing agent. Again, if no reaction occurred, indicate "no reaction"arrow_forward1. About what volume does 0.15 mol of 2-methylcyclohexanol occupy at room temperature? 15.0 mL 18.5 mL 20.0 mLarrow_forward
- You have a mixture of an aryl halide and a carboxylic acid that you wish to separate (both are solids). Both are soluble in diethyl ether. Explain ALL the steps you would take to obtain the two compounds in pure form from your sample.arrow_forwardHelparrow_forwardDraw the structure(s) of the major organic product(s) of the following reaction. an 1. in benzene 2. aqueous HCIarrow_forward
- What is the IUPAC name for the following 2. What is the IUPAC name for the compound? following compound? u 1. ГОН 2-methylpentanoic acid 3-methylpentanoic acid 2-methylhexanoic acid 3-methylhexanoic acid None of these What is the IUPAC name for the following 4. compound? A. B. C. D. 3. A. B. C. D. E. sec-butyl ethanoate ethyl 3-methylpentanoate 3-methylbutyl ethanoate ethyl 3-methylbutanoate none of these A BUDE A. B. C. A. B. ABCDE What is the IUPAC name for the following compound? CI C. D. E. a-methylbutyryl chloride B-methylbutyryl chloride y-methylbutyryl chloride 2-methylbutanoyl chloride 3-methylbutanoyl chloride propanoic anhydride butanoic anhydride propionic anhydride pentanoic anhydride butyric anhydridearrow_forwardSelect all compounds that are able to deprotonate ethanol, EtOH, to the extent that the neutralization reaction is product-favored at equilibrium. a. Na2s b. NaNH2 С. BuLi d. NaF e. NaCN f. NaCH3CO2 g. NH3 h. CH3LIarrow_forwardWhat is the functional group of propanoic acid? How do we know if it's soluble in water or not using the flowchart that is attached. which test should be performed using the flowchart. Is propanoic acid a ketone, aldehyde, ester or alcohol and how did you know?what would be the most efficient series of solubility and functional group tests that would identify the functional group? Also what could be the sources of error in this experiment? What could occur that would give false positives, false negatives, or incorrect interpretations?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY