
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Given the H-NMR spectra, identify the peaks that can be represented for 2-Naphthyl-Butylether.
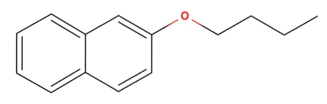
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts the chemical structure of 2-butoxynaphthalene.
### Description
- **Naphthalene Ring**: The structure is based on two fused benzene rings, known as a naphthalene ring, which is a common aromatic hydrocarbon.
- **Oxygen Atom**: Attached to one of the outer carbon atoms is an oxygen atom (highlighted in red), indicating an ether linkage.
- **Butoxy Group**: The oxygen is connected to a butoxy group, a chain of four carbon atoms connected linearly. This group extends to the right of the naphthalene structure.
### Explanation of Components
- **Aromatic Ring**: The naphthalene provides the aromatic character, making the compound part of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
- **Ether Linkage**: The presence of the ether (oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms) classifies this compound as an aromatic ether, a type of organic functional group.
Overall, this compound is used in certain industrial applications and can serve as an intermediate in various chemical syntheses.
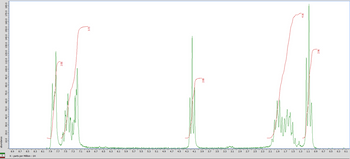
Transcribed Image Text:The image presents a spectral graph commonly used in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The x-axis is labeled "X: parts per Million 1H," which indicates the chemical shift in parts per million (ppm) relevant to hydrogen-1 nuclei. This scale is typical for analyzing the environment of hydrogen atoms in molecular structures.
The y-axis, labeled "Amplitude," measures the signal intensity of various hydrogen environments. Peaks on the graph represent distinct hydrogen environments within a sample.
Two plots are visible on the graph:
1. **Green Plot**: This represents the main NMR spectrum showing the peaks corresponding to different hydrogen environments. The tallest peaks indicate higher concentrations or stronger signals from those particular hydrogen atoms.
2. **Red Plot**: This usually denotes a reference or baseline correction applied to the spectrum to improve accuracy.
Notable features on the graph include:
- A set of peaks around 7.1 to 8.0 ppm, typically associated with aromatic hydrogen environments.
- A significant peak near 4.1 ppm, which may correlate with hydrogens in an alcohol or ether linkage.
- An intense multiplet between 1.0 and 2.0 ppm, often indicative of alkane hydrogens.
The small numbers in red next to the peaks (e.g., 2.35, 3.72) likely represent integral or relative intensity data, useful for quantifying the number of hydrogens in a specific environment. This type of analysis helps in determining the structure and composition of chemical compounds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2) For each of the following pairs of compounds, name one absorption band that can be used to distinguish between them. State what the bond is (bond order, between which 2 atoms), and approximately where it appears in the IR spectrum (in cm ¹). b) HO 1-hexanol OH phenol H₂N 1-butanamine ethyl acetate cyclohexane OH hexanoic acid LOH cyclohexanol NH₂ butanamide diethyl ether cyclohexenearrow_forwardComparison of specific functional group diagnostic peaks (C=O carboxylic acid, C-H, O-H carboxylic acid, O-H phenol, C=C) between Literature and Experimental spectra.arrow_forwardButanal and methylpropanal give slightly different mass spectra. Both give a molecular ion peak at m/z = 72, but butanal gives four other peaks whereas methylpropanal only gives three. State the species responsible for the four other peaks in the mass spectrum of butanal and write equations to show their formation from the molecular ion.arrow_forward
- Which of the following compounds will display a singlet, a triplet and a quartet in its ¹H NMR spectrum? 3-chloropentane O 2-chloro-4-methylpentane 3-chloro-3-methylpentane O 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylbutane 3-chloro-2-methylpentanearrow_forwardBy examining the carbon NMR spectra of 1,1-dichlorocyclohexane and cis-1,2- dichlorocyclohexane, what TWO things would you look for to distinguish between the spectra. Use structures to explain your answer.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forward
- What fragment is responsible for the base peak in the MS spectra of 4-phenyl-2-butanone, 1-phenyl-1-butanone, and 1-phenyl-2-butanonearrow_forwardHow does the proton (1H) NMR of the methyl benzoate reagent compare to the methyl 3-nitrobenzoate product? Include (or illustrate) the NMR plots and peak assignments for each please type out so i can read clearlyarrow_forwardWhich of these choices best describes the interpretation of the following peak that may be recorded in a 'H NMR spectrum? 2.5 8 (2H, d). The underlined hydrogen atom is intended to be the one producing the peak that we are interpreting. O=C-CH,CO2H O=C-CH2CHX2 O=C-CH2CH2X O=C-CH2CH3 None of these interpretations describes this peak.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY