
Concept explainers
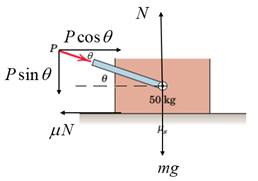
The 50-kg block rests on the horizontal surface, and a force
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Introduction to Heat Transfer
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Heating Ventilating and Air Conditioning: Analysis and Design
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
- The 60-lb plank rests on a frictionless roller at A, and the 20-lb triangular support BD. Both bodies are homogenous. The coefficients of static friction are 0.4 at B and 0.3 at D. Determine the largest force P that can be applied to the plank without initiating motion.arrow_forwardThe 600-lb cable spool is placed on a frictionless spindle that has been driven into the ground. If the force required to start the spool rotating is F = 160 lb, determine the coefficient of friction between the ground and the spool. Neglect the diameter of the spindle compared to the diameter of the spool.arrow_forwardThe force P is applied to the 37-kg block when it is at rest. Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force exerted by the surface on the block if (a) P = 0, (b) P = 107 N, and (c) P = 168 N. (d) What value of P is required to initiate motion up the incline? The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the block and the incline are us = 0.19 and k = 0.16, respectively. The friction force is positive if up the incline, negative if down the incline. Answers: (a) F= 37 kg 12° i (b) F= i (c) F= i (d) P= i 21° H.= 0.19 H₁ = 0.16 zzz N N N Narrow_forward
- The man is pedaling his bicycle at a constant speed up a slippery slope of 5%. The man and the bicycle have a total mass of 82 kg centered at G. If the rear wheel is about to slip, find the coefficient of friction u between the tire and the road. If the coefficient of friction were doubled, what friction force would act on the rear wheel? (Why can we neglect the friction under the front wheel?)arrow_forwardDetermine the force P that will cause impending motion. Also determine location of the resultant force acting on the crate, measured from the point A. (M=200 kg, a=1 m, b=2m, c=0.5 m, d34, e=3 and coefficient of friction is 0.3) aarrow_forwardThe force Pis applied to the 52-kg block when it is at rest. Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force exerted by the surface on the block if (a) P = 0, (b) P = 165 N, and (c) P = 265 N. (d) What value of P is required to initiate motion up the incline? The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the block and the incline are u, = 0.20 and Uk = 0.15, respectively. The friction force is positive if up the incline, negative if down the incline. 52 kg 19 H, = 0.20 H = 0.15 13 Answers: (a) F= -115 (b) F= i 41.3 N (c) F= i 136 N (d) P= i 44.9 Narrow_forward
- Yes Ⓒ No Movers are trying to set up an art gallery. They attempt to drag a human-size statue of a soda can with mass m = 120 kg by tying a rope around it. Determine if the movers can drag the statue along the floor without it tipping if the coefficients of static friction and kinetic friction are found to be μ = 0.37 and Hk = 0.26, respectively. What is the maximum force the movers can apply without tipping the statue? The can has a height of h = 1.9 m and the rope is tied 1 m off the ground. Assume the statue to be a solid cylinder with radius r = 0.2 m and constant density. Can the statue be dragged without tipping? 313.44 y = 1.7 y x N F Ftip If the movers can apply the force required for the statue to slip, where is the maximum height they should tie the rope to safely drag the statue? x m Å UBC Engineeringarrow_forward3. Car A has a mass of 1.4 Mg with center of gravity at point G as shown in Fig. 3. If car B exert a 2 kN, determine whether the force is sufficient to move car A. The static and dynamic friction coefficients between tyre and the road are μ, = 0,5 and μ = 0,35. Assume the surface of car B bumper to be frictionless. 0.5 m 0.8 m 0.8 mi 2 kN 0.4 m Gambar 3. Tyre-Road frictionarrow_forwardThe main body of the cabinet weighs 15 kg, while the upper rectangular portion weighs 2.5 kg. Assume the following values for coefficients of friction between the cabinet and the floor: μs = 0.26 and μk = 0.19. Knowing that the force P applied by Joey’s shoulder to the cabinet is horizontal: If Joey’s horizontal leaning force is 44.5 N, which of the following best describes the motion of the cabinet? slipping, not moving, tipping, or impending to slip?arrow_forward
- The coefficient of static friction between the 50-kg crate and the ramp is μs = 0.35. The unstretched length of the spring is 800 mm, and the spring constant is k = 660 N/m. Determine the following: 1 The normal force acting on the crate is Blank 1 N. 2 The friction force acting on the crate is Blank 2 N. 3 The minimum value of x at which the crate can remain stationary on the ramp is Blank 3 mm.arrow_forwardThe force P is applied to the 61-kg block when it is at rest. Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force exerted by the surface on the block if (a) P = 0, (b) P = 239 N, and (c) P = 387 N. (d) What value of P is required to initiate motion up the incline? The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the block and the incline are us = 0.27 and μ = 0.24, respectively. The friction force is positive if up the incline, negative if down the incline. Answers: (a) F= 61 kg 16° i (b) F= i (c) F= i (d) P= i 25 H₂ = 0.27 H = 0.24 z z z Narrow_forward1. The two 890 N blocks are pushed apart by the 150 wedge of negligible weight. The angle of static friction is 12° at all surfaces. Determine the force P required to start the blocks moving. 890N 890Narrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
