
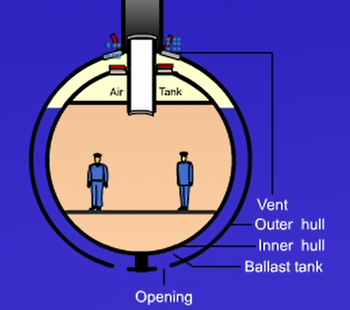
When the submarine is on the surface, its ballast tanks are filled with air. As the submarine dives, the ballast tanks are flooded with water and the air in the ballast tanks is vented from the submarine. The submarine descends from sea level and holds at a constant depth of 3,500m.
Background Information
- Submarine
- Volume is 450 m3
- Mass (excluding weight in ballast tank) is 400 tons
- Outer haul
- Mass is 40 tons
- Thickness is 15 cm
- Exterior surface area is 200 m2
- Specific heat capacity is 420 J/kg/K
- Latent heat of fusion is 250 kJ/kg
- Temperature at
- surface (depth of 0 m) is 25°C
- depth of 3,500 m
- internal of the outer haul (next to ballast tank) is 30°C (Refer to diagram)
- external of the outer haul is 10°C (Refer to diagram)
- Thermal conductivity is 80 kW/m/K
- Emissivity of 0.9
- Ballast Tank at a depth of 3,500 m
- Temperature at is 30°C
- Seawater
- Specific gravity of 1.05
- Surrounding temperature at a depth of 3,500 m is 4°C
- Convective heat transfer coefficient for free convection is 75 W/m2/K
Questions:
1a) When the submarine holds at the constant depth of 3,500m, calculate the
-
- buoyant force on the submarine.
- weight of seawater in the ballast tank.
- seawater pressure.
1b) When seawater flows into the bottom opening at 10 m/s, calculate the velocity of the seawater level (8m above the bottom of the submarine) inside the ballast tank (v on diagram).
1c) Calculate the net force on the submarine circular hatch door (10m above the bottom of the submarine) with a radius of 0.5m. The air pressure inside the submarine below the hatch door is 101.3 kPa.
1d) Calculate the change in heat energy of the submarine’s outer haul, when it descends from the surface to a depth of 3,500m (with an average temperature of 20°C).
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

can i know for subpart c, why the value of the pressure inside is 150101.3 kPa? as the question is finding for the net force in the hatch door and the air inside acting on the hatch door is only 101.3 kPa?
can i know for subpart c, why the value of the pressure inside is 150101.3 kPa? as the question is finding for the net force in the hatch door and the air inside acting on the hatch door is only 101.3 kPa?
- The test tube opens at 293 K with 15 cm Hg at the bottom, and 7.5 cm of water above the Hg. Calculate the pressure at the bottom of the tube if the atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg. Use the density of 13:55 g / cm3 for Hg and 0998 g / cm3 to air.Berikan answers in terms of dyne / cm2,psia, and kN / m2 • (see conversion table). a. … KPa. b. … Dyne / cm2. c. … Psia.arrow_forwardChemistry The contact angle for water in a clean glass is zero. Calculate the surface tension of waterin a 0.3 mm diameter vertical tube if the water rises to a height 4.96 cm above the liquidoutside the tube, knowing that specific gravity of water equals 998.2 kg/m 3 and theacceleration due to gravity equals 9.806 m/sec2arrow_forwardwhat is the answer for number 3?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





