The vapor pressures of ethanol (C₂H₂OH) and 1-propanol (C₂H,OH) at 35 °C are 100. mmHg and 37.6 mmHg, respectively. Assume ideal behavior and calculate the partial pressures of ethanol and 1-propanol at 35 °C over a solution of ethanol in 1-propanol, in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.317. Be sure each of your answer entries has the correct number of significant digits. Part 1 of 2 P ethanol mmHg x10 Part 2 of 2 P₁ mmHg 1-propanol x10 The osmotic pressure of 1.77 × 102 M solutions of CaC₁₂ and urea at 25 °C are 1.07 atm and 0.433 atm, respectively. Calculate the van't Hoff factor for the CaCl2 solution. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. i = - I ☐ x10
The vapor pressures of ethanol (C₂H₂OH) and 1-propanol (C₂H,OH) at 35 °C are 100. mmHg and 37.6 mmHg, respectively. Assume ideal behavior and calculate the partial pressures of ethanol and 1-propanol at 35 °C over a solution of ethanol in 1-propanol, in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.317. Be sure each of your answer entries has the correct number of significant digits. Part 1 of 2 P ethanol mmHg x10 Part 2 of 2 P₁ mmHg 1-propanol x10 The osmotic pressure of 1.77 × 102 M solutions of CaC₁₂ and urea at 25 °C are 1.07 atm and 0.433 atm, respectively. Calculate the van't Hoff factor for the CaCl2 solution. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. i = - I ☐ x10
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter12: Solutions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12.94QE
Related questions
Question
Please help me with this homework i tried solving it and it is due today
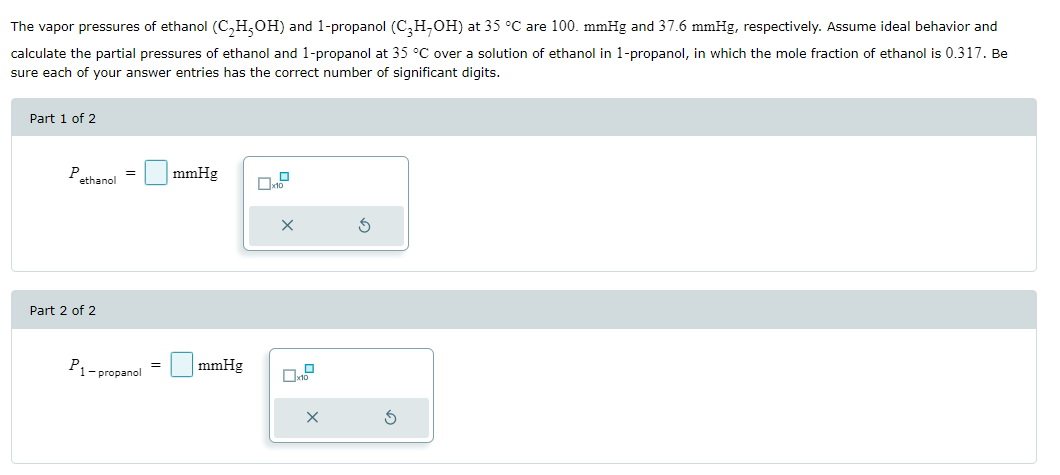
Transcribed Image Text:The vapor pressures of ethanol (C₂H₂OH) and 1-propanol (C₂H,OH) at 35 °C are 100. mmHg and 37.6 mmHg, respectively. Assume ideal behavior and
calculate the partial pressures of ethanol and 1-propanol at 35 °C over a solution of ethanol in 1-propanol, in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.317. Be
sure each of your answer entries has the correct number of significant digits.
Part 1 of 2
P
ethanol
mmHg
x10
Part 2 of 2
P₁
mmHg
1-propanol
x10
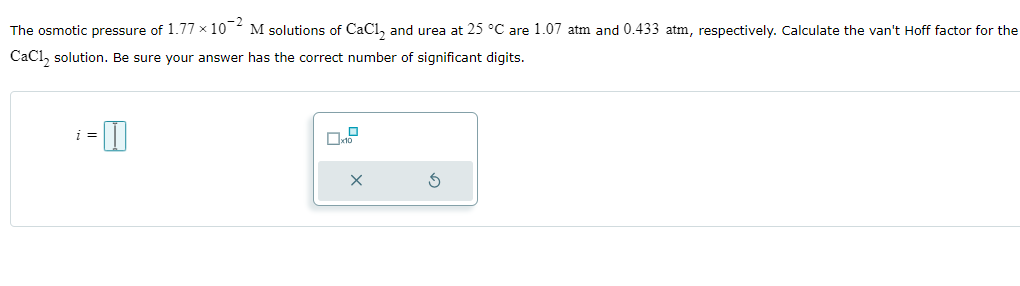
Transcribed Image Text:The osmotic pressure of 1.77 × 102 M solutions of CaC₁₂ and urea at 25 °C are 1.07 atm and 0.433 atm, respectively. Calculate the van't Hoff factor for the
CaCl2 solution. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.
i =
- I
☐ x10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 1 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning