
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
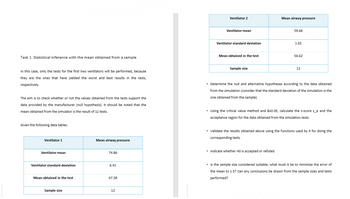
Transcribed Image Text:Task 1. Statistical inference with the mean obtained from a sample
Ventilator 2
Mean airway pressure
Ventilator mean
59.66
Ventilator standard deviation
1.65
Mean obtained in the test
56.62
Sample size
12
In this case, only the tests for the first two ventilators will be performed, because
they are the ones that have yielded the worst and best results in the tests,
respectively.
The aim is to check whether or not the values obtained from the tests support the
data provided by the manufacturer (null hypothesis). It should be noted that the
mean obtained from the simulator is the result of 12 tests.
Given the following data tables:
Ventilator 1
Mean airway pressure
Ventilator mean
74.86
Ventilator standard deviation
6.41
Determine the null and alternative hypotheses according to the data obtained
from the simulation (consider that the standard deviation of the simulation is the
one obtained from the sample).
Using the critical value method and E=0.05, calculate the z-score z_a and the
acceptance region for the data obtained from the simulation tests.
* Validate the results obtained above using the functions used by R for doing the
corresponding tests.
Indicate whether HO is accepted or refuted.
▸ Is the sample size considered suitable, what must it be to minimize the error of
the mean to 1.5? Can any conclusions be drawn from the sample sizes and tests
performed?
Mean obtained in the test
67.38
Sample size
12
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Need help with 5,5,6arrow_forwardDylan has collected 20 quarters and wants to compare the age of each coin to the age of all coins in the US. Select all the reasons why a z-test should not be used. Choose all that apply: 1. The sample standard deviation cannot be calculated 2. The sample size is >10 3. We do not have the population standard deviation 4. The sample size is <30 5. The population is <500arrow_forwardThis assignment is worth 1 points. The extra point will be added to your overall course grade. For example: if you receive an 88% in the course you can receive up to 1 point giving you a new score of 89%. The following rubric will be used. 0.25 point for drawing the normal distribution curve with the mean value labeled on the curve and the appropriate area shaded. 0.25 point for determining the value of the standard deviation of the sample mean. 0.5 point for finding the correct probability. All work must be shown in order to receive any credit. Please upload your completed assignment here. The length of time taken on the SAT for a group of students is normally distributed with a mean of 2.5 hours and a standard deviation of 0.25 hours. A sample size of n = 60 is drawn randomly from the population. Find the probability that the sample mean is between two hours and three hours.arrow_forward
- I. There are two samples with means 15 and 18. Both of those samples consist of 24 observations. Sample standard deviations are equal to 4 in both cases. If you want to test whether the difference between the mean in the first and the mean in the second population is equal to 0, what is your decision at the .01 level?arrow_forwardChoose the appropriate statistical test. When computing, be sure to round each answer as indicated. A dentist wonders if depression affects ratings of tooth pain. In the general population, using a scale of 1-10 with higher values indicating more pain, the average pain rating for patients with toothaches is 6.8. A sample of 30 patients that show high levels of depression have an average pain rating of 7.1 (variance 0.8). What should the dentist determine? 1. Calculate the estimated standard error. (round to 3 decimals). [st.error] 2. What is thet-obtained? (round to 3 decimals). 3. What is the t-cv? (exact value) 4. What is your conclusion? Only type "Reject" or Retain"arrow_forwardListed below are systolic blood pressure measurements (mm Hg) taken from the right and left arms of the same woman. Assume that the paired sample data is a simple random sample and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Use a 0.05 significance level to test for a difference between the measurements from the two arms. What can be concluded? Right arm Left arm 150 142 120 131 167 160 179 156 In this example, Hd is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the measurement from the right arm minus the measurement from the left arm. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? O A. Ho: Hd = 0 H₁: Hd 0 Since the P-value is than the significance level, the null hypothesis. There sufficient evidence to support the claim of a difference in measurements between the two arms.arrow_forward
- Step 1 of 3. State the null and alternative hypotheses for the test. Step 2 of 3. Compute the value of the test statistic. Round your answer to three decimal places Step 3 of 3. Draw a conclusion and interpret the decision.arrow_forwardsolve question 3 pleasearrow_forwardAn experiment was conducted to determine whether giving candy to dining parties resulted in greater tips. The mean tip percentages and standard deviations are given in the accompanying table along with the sample sizes. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Complete parts (a) and (b). ... Question content area top right Part 1 μ n x s No candy μ1 36 18.61 1.39 Two candies μ2 36 21.26 2.34 * find the t stat * find the p value * State the conclusion * Construct a confidence interval suitable for testing the claim that the two samples are from populations with the same mean.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman