
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
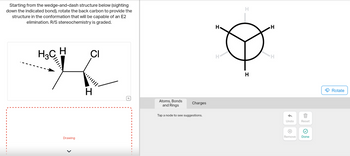
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website**
---
### Understanding E2 Elimination Reactions
**Objective:**
Transform the given wedge-and-dash molecular structure to align for an E2 elimination reaction, ensuring the correct R/S stereochemistry.
#### Instructions:
1. **Starting Structure:**
- **Diagram Description:** The initial molecule is represented in a wedge-and-dash 3D model. It consists of a central carbon atom attached to a methyl group (CH₃), a hydrogen atom (H), a chlorine atom (Cl), and another hydrogen atom. The wedge and dash notation indicates the spatial arrangement of these substituents.
2. **Task:**
- Rotate the back carbon along the specified bond (indicated by an arrow) to achieve the necessary anti-periplanar conformation needed for an E2 elimination reaction.
3. **Concept Overview:**
- **E2 Mechanism:** In an E2 elimination, a hydrogen atom and a leaving group (e.g., Cl) must be in an anti-periplanar arrangement (180 degrees from each other) to facilitate the elimination reaction to form a double bond.
- **Stereochemistry:** Analyze the R/S configuration to ensure that the product maintains the correct stereochemistry.
#### Visualization:
**Conversion Tool:**
- The accompanying circle diagram helps visualize the rotations needed. In this top-down view of the molecule, each H (hydrogen) appears at the vertices of the triangle framework. By adjusting these positions, learners can achieve the desired orientation for E2 elimination.
**Interactive Elements:**
- **Rotate:** Use the rotation tool to adjust the molecule.
- **Atoms, Bonds, and Rings:** Select any node to receive guidance on modifications.
- **Tool Functions:** Reset to the initial state or undo changes as necessary.
#### Final Notes:
By completing this exercise, students will gain a deeper understanding of molecular geometry and reaction mechanisms, crucial for mastering organic chemistry principles.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET) is the active ingredient in many insect repellent preparations. Following is one of the steps in its synthesis. In the box below draw the structure of the product of this reaction. H3C MgBr 1. CO2 2. H30* product • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • Do not include lone pairs in your answer. They will not be considered in the grading. • Draw the Grignard reagent as a covalent magnesium bromide. P ору aste O O O- []# Previous Next Email Instructor Save and Exitarrow_forwardDraw the structure for an alkene that gives the following reaction product. 1. Hg(OАc)2, Н2О ? -CHCH3 2. NABH4 ОН Ignore alkene stereochemistry. You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. Visited opy aste ChemDoodlearrow_forwardThe reaction shown proceeds via a single transition state with a trigonal bipyramidal geometry. C1 C2 Br: + H3C 0: Two curved arrows are required to indicate all of the bond-making and bond-breaking processes in this reaction. Where should one of the arrows be drawn, if CH3O is the nucleophile? from a Br LP to the O atom from C1 to the O atom from C2 to the O atom from the C-O bond to Br from an O LP to C1 from an O LP to C2arrow_forward
- nent/takeCovalentActivity.do?16cal assigi [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Draw a structural formula for the major organic anion formed when 2- ethylbutanal is reacted with Tollens' reagent. You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • If no reaction occurs, draw the organic starting material. P. opy aste CH4 ChemDoodle Previous Nexarrow_forward44a) Draw the bond-line structure of 1,4-dimethyl-cyclohexa-1,3-diene here: STRUCTURE: b) Circle all the sp²-hybridized carbons in your drawing of the structure. c) In the spaces below, draw two potential products from a chlorination reaction (addition of Cl2) with your first structure Product 1: Product 2:arrow_forwardch-1 Dont provide handwriting solutionarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula for the major product of the reaction shown. Cl₂ H₂O Show product stereochemistry IF the reactant alkene has both carbons of the double bond within a ring. • Do not show stereochemistry in other cases. If the reaction produces a racemic mixture, just draw one stereoisomer. 8 Sn [F ChemDoodleⓇarrow_forwardIn the problem we are considering the stereoisomers of 4-bromo-3-methoxy-2-methylhexane. Assign the stereochemistry for the molecule represented in each diagram. Within each stereoisomer pool rank the conformers from most stable to least stable. Hints: You may not have a representation for each different energy conformer. You may have more than one that represents the same energy. 41 B2₂ Et Br OEt HA HE Eto Et DE+ " Br 4 BV Et * # Br I ¡Et Ht Br Eto Et Et Et H 4 Br # o Et с G Et 4 E+ DEX off # Et H Exactarrow_forwardDraw the structure of each isomer.arrow_forward
- An alkene having the molecular formula C6H₁2 is treated sequentially with ozone (03) and zinc/acetic acid to give the product/s shown. O Draw a structural formula for the alkene. H3C 1 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. + ▾ CH3 will n [F ChemDoodleⓇ 16arrow_forwardWhat is the major monobromination product of the following reaction? Disregard stereoisomers. What is the anticipated percent yield of the major product (as a percentage of all the monobrominated products)?arrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for the major product of the reaction shown. Br2 =CHCH2CH3 H20 • Show product stereochemistry IF the reactant alkene has both carbons of the double bond within a ring. • Do not show stereochemistry in other cases. • If the reaction produces a racemic mixture, just draw one stereoisomer. aste ChemDoodle Previous Next Save and Exi tv MacBook Air DD 80 888 F11 F12 F9 F10 F7 F8 F5 F6 F3 F4 & ( ) #3 $ % %3D 3 4 6 7 8 9. { } P E Y U D G H J K F > .. .. Rarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY