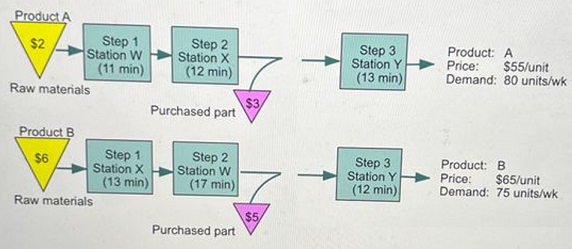
Canine Kennels Company (CKC) manufactures two different types of dog chew toys (A and B, sold in 1,000-count boxes) that are manufactured and assembled on three different workstations (W, X, and Y) using a small-batch process (see the figure below). Batch setup times are negligible. The flowchart denotes the path each product follows through the manufacturing process, and each product's price, demand per week, and processing times per unit are indicated as well. Purchased parts and raw materials consumed during production are represented by inverted triangles. CKC can make and sell up to the limit of its demand per week; no penalties are incurred for not being able to meet all the demand. Each workstation is staffed by a worker who workstation alone and is paid $6 per hour. Total labor costs per week are fixed. Variable overhead costs are $3,500/week. The plant operates one 8-hour shift per day, or 40 hours/week. dedicated to work on that Q Q Product A $2 Step 1 Station W (11 min) Raw materials Product B $6 Step 1 Station X (13 min) Raw materials Step 2 Station X (12 min) Purchased part Step 2 Station Wi (17 min) Purchased part $3 $5 Step 3 Station Y (13 min) Step 3 Station Y (12 min) Which of the three workstations, W, X, or Y has the highest aggregate workload, and thus serves as the bottleneck for CKC? response as an integer.) Product: A Price: $55/unit Demand: 80 units/wk Product: B Price: $65/unit Demand: 75 units/wk G with a total load time of minutes. (Enter your
Canine Kennels Company (CKC) manufactures two different types of dog chew toys (A and B, sold in 1,000-count boxes) that are manufactured and assembled on three different workstations (W, X, and Y) using a small-batch process (see the figure below). Batch setup times are negligible. The flowchart denotes the path each product follows through the manufacturing process, and each product's price, demand per week, and processing times per unit are indicated as well. Purchased parts and raw materials consumed during production are represented by inverted triangles. CKC can make and sell up to the limit of its demand per week; no penalties are incurred for not being able to meet all the demand. Each workstation is staffed by a worker who workstation alone and is paid $6 per hour. Total labor costs per week are fixed. Variable overhead costs are $3,500/week. The plant operates one 8-hour shift per day, or 40 hours/week. dedicated to work on that Q Q Product A $2 Step 1 Station W (11 min) Raw materials Product B $6 Step 1 Station X (13 min) Raw materials Step 2 Station X (12 min) Purchased part Step 2 Station Wi (17 min) Purchased part $3 $5 Step 3 Station Y (13 min) Step 3 Station Y (12 min) Which of the three workstations, W, X, or Y has the highest aggregate workload, and thus serves as the bottleneck for CKC? response as an integer.) Product: A Price: $55/unit Demand: 80 units/wk Product: B Price: $65/unit Demand: 75 units/wk G with a total load time of minutes. (Enter your
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter12: Queueing Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 59P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:K
Canine Kennels Company (CKC) manufactures two different types of dog chew toys (A and B, sold in 1,000-count boxes) that are manufactured and assembled on three different workstations (W, X,
and Y) using a small-batch process (see the figure below). Batch setup times are negligible. The flowchart denotes the path each product follows through the manufacturing process, and each
product's price, demand per week, and processing times per unit are indicated as well. Purchased parts and raw materials consumed during production are represented by inverted triangles. CKC
can make and sell up to the limit of its demand per week; no penalties are incurred for not being able to meet all the demand. Each workstation is staffed by a worker who is dedicated to work on that
workstation alone and is paid $6 per hour. Total labor costs per week are fixed. Variable overhead costs are $3,500/week. The plant operates one 8-hour shift per day, or 40 hours/week.
Product A
$2
Step 1
Station W
(11 min)
Raw materials
Product B
$6
Raw materials
Step 1
Station X
(13 min)
Step 2
Station X
(12 min)
Purchased part
Step 2
Station W
(17 min)
Purchased part
$3
$5
G
Step 3
Station Y
(13 min)
Step 3
Station Y
(12 min)
Which of the three workstations, W, X, or Y has the highest aggregate workload, and thus serves as the bottleneck for CKC?
response as an integer.)
Product: A
Price:
$55/unit
Demand: 80 units/wk
Product: B
Price: $65/unit
Demand: 75 units/wk
with a total load time of
Workstation Y
Workstation W
Workstation X
minutes. (Enter your
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given-
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,