(c) (1 ) Fluoroacetate, prepared commercially for rodent control, is also produced by a South Afri- can plant. After entering a cell, fluoroacetate is converted to fluoroacetyl-CoA in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme acetate thiokinase: F-CH2COO¯ + COA-SH + ATP F-CH2CO-SCOA + AMP + PPj The toxic effect of fluoroacetate was studied in an experiment using intact isolated rat heart. After the heart was perfused with 0.22 mM fluoroacetate, the measured rate of glucose uptake and glycolysis decreased, and glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate accumulated. Examination of the cit- ric acid cycle intermediates revealed that their concentrations were below normal, except for citrate, with a concentration 10-fold higher than normal. Where did the block in the citric acid cycle occur? What caused citrate to accumulate and the other cycle intermediates to be depleted? Explain. Why does it block the citric acid cycle? Fluoroacetyl-CoA is enzymatically transformed in the citric acid cycle. Name and draw the structure of the end product of fluoroacetate metabolism? How might the inhibition be overcome? Explain.
(c) (1 ) Fluoroacetate, prepared commercially for rodent control, is also produced by a South Afri- can plant. After entering a cell, fluoroacetate is converted to fluoroacetyl-CoA in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme acetate thiokinase: F-CH2COO¯ + COA-SH + ATP F-CH2CO-SCOA + AMP + PPj The toxic effect of fluoroacetate was studied in an experiment using intact isolated rat heart. After the heart was perfused with 0.22 mM fluoroacetate, the measured rate of glucose uptake and glycolysis decreased, and glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate accumulated. Examination of the cit- ric acid cycle intermediates revealed that their concentrations were below normal, except for citrate, with a concentration 10-fold higher than normal. Where did the block in the citric acid cycle occur? What caused citrate to accumulate and the other cycle intermediates to be depleted? Explain. Why does it block the citric acid cycle? Fluoroacetyl-CoA is enzymatically transformed in the citric acid cycle. Name and draw the structure of the end product of fluoroacetate metabolism? How might the inhibition be overcome? Explain.
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter19: The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 22P: Study Figure 19.18 and decide which of the following statements is false. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is...
Related questions
Question
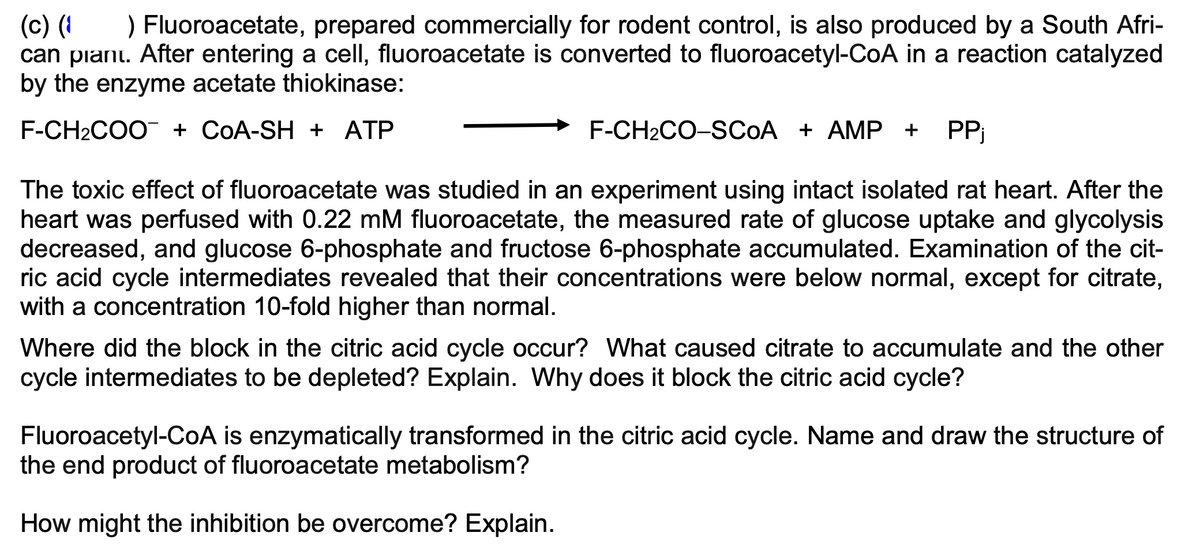
Transcribed Image Text:(c) (1
) Fluoroacetate, prepared commercially for rodent control, is also produced by a South Afri-
can plant. After entering a cell, fluoroacetate is converted to fluoroacetyl-CoA in a reaction catalyzed
by the enzyme acetate thiokinase:
F-CH2COO¯ + COA-SH + ATP
F-CH2CO-SCOA + AMP + PPj
The toxic effect of fluoroacetate was studied in an experiment using intact isolated rat heart. After the
heart was perfused with 0.22 mM fluoroacetate, the measured rate of glucose uptake and glycolysis
decreased, and glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate accumulated. Examination of the cit-
ric acid cycle intermediates revealed that their concentrations were below normal, except for citrate,
with a concentration 10-fold higher than normal.
Where did the block in the citric acid cycle occur? What caused citrate to accumulate and the other
cycle intermediates to be depleted? Explain. Why does it block the citric acid cycle?
Fluoroacetyl-CoA is enzymatically transformed in the citric acid cycle. Name and draw the structure of
the end product of fluoroacetate metabolism?
How might the inhibition be overcome? Explain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning