
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ent/Assignment-Responses/submit?dep=33382244&tags=autosave #question5223788_4
D
Finish update
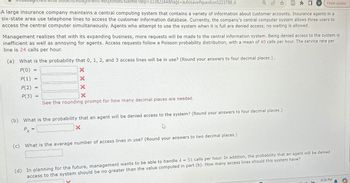
A large insurance company maintains a central computing system that contains a variety of information about customer accounts. Insurance agents in a
six-state area use telephone lines to access the customer information database. Currently, the company's central computer system allows three users to
access the central computer simultaneously. Agents who attempt to use the system when it is full are denied access; no waiting is allowed.
Management realizes that with its expanding business, more requests will be made to the central information system. Being denied access to the system is
inefficient as well as annoying for agents. Access requests follow a Poisson probability distribution, with a mean of 40 calls per hour. The service rate per
line is 24 calls per hour.
(a) What is the probability that 0, 1, 2, and 3 access lines will be in use? (Round your answers to four decimal places.).
P(O)
P(1)
P(2)
-
X
P(3)
=
X
See the rounding prompt for how many decimal places are needed.
(b) What is the probability that an agent will be denied access to the system? (Round your answers to four decimal places.)
Pk =
(c)
X
What is the average number of access lines in use? (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
51 calls per hour. In addition, the probability that an agent will be denied
(d) In planning for the future, management wants to be able to handle
access to the system should be no greater than the value computed in part (b). How many access lines should this system have?
=
ר
8:58 PM
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Determine the given variables.
VIEW Step 2: Find the probability of 0, 1, 2, 3 access line will be in use.
VIEW Step 3: Find the probability that an agent will be denied access to the system.
VIEW Step 4: Find the average no. of access lines in use.
VIEW Step 5: Find the no. of access lines if lamda = 51 calls per hour.
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 12 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- An inventor has developed a system that allows visitors to museums, zoos, and other attractions to get information at the touch of a digital code. For example, zoo patrons can listen to an announcement (recorded on a microchip) about each animal they see. It is anticipated that the device would rent for $3.00 each. The installation cost for the complete system is expected to be about $400,000. The Milwaukee Zoo is interested in having the system installed, but management is uncertain about whether to take the risk. A financial analysis of the problem indicates that if more than 10% of the Zoo visitors rent the system the zoo will make a profit. To help make the decision, a sample of 400 zoo visitors is given details of the system’s capabilities and cost. Forty eight people say they would rent the device. c). Estimate the actual percentage of the visitors who would rent the system using a 98% confidence interval using Minitab.arrow_forwardHillary and Adams, Inc., is a privately owned firm located in Atlanta that serves as the regional distributor of natu-ral food products for Georgia, Kentucky, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee. They are particularlywell known for their unique blend of fiery hot Habanera sauces. Every week, a truck leaves the large distributioncenter in Atlanta to stock local warehouses located in Charlotte, North Carolina; Charleston, South Carolina;Columbia, South Carolina; Knoxville, Tennessee; Lexington, Kentucky; and Raleigh, North Carolina. The truckvisits each local warehouse only once and returns to Atlanta after all the deliveries have been completed. Thedistance between any two cities in miles is given below John Jensen, vice president of logistics at Hillary and Adams, Inc., is worried about the rising fuel costs.With a reduction in operating budgets, he is interested in finding a route that would minimize the distance trav-eled by the truck.Use the NN heuristic to identify a…arrow_forwardConsider a remote town in which two restaurants, All-You-Can-Eat Café and GoodGrub Diner, operate in a duopoly. Both restaurants disregard health and safety regulations, but they continue to have customers because they are the only restaurants within 80 miles of town. Both restaurants know that if they clean up, they will attract more customers, but this also means that they will have to pay workers to do the leaning. If neither restaurant cleans, each will earn $14,000; alternatively, if they both hire workers to clean, each will earn only $11,000. However, if one cleans and the other doesn't, more customers will choose the cleaner restaurant; the cleaner restaurant will make $18,000, and the other restaurant will make only $6,000. Complete the following payoff matrix using the information just given. (Note: All-You-Can-Eat Café and GoodGrub Diner are both profit-maximizing firms.) All-You-Can-Eat Café $ Cleans Up Doesn't Clean Up $ Cleans Up $ 81°F Sunny $ GoodGrub Diner $ $ If…arrow_forward
- Mid-West Publishing Company publishes college textbooks. The company operates an 800 telephone number whereby potential adopters can ask questions about forthcoming texts, request examination copies of texts, and place orders. Currently, two extension lines are used, with two representatives handling the telephone inquiries. Calls occurring when both extension lines are being used receive a busy signal; no waiting is allowed. Each representative can accommodate an average of 11 calls per hour. The arrival rate is 22 calls per hour. How many extension lines should be used if the company wants to handle 90% of the calls immediately?4 lines What is the average number of extension lines that will be busy if your recommendation in part (a) is used? Round your answer to four decimal places.L = ?????????? What percentage of calls receive a busy signal for the current telephone system with two extension lines? Round your answer to two decimal places.40 %arrow_forwardA real estate investment trust (REIT) owns first-class office properties in selected markets. According to its website, the occupancy rates last year for its holdings in four major cities are available below. Complete parts a through c below.arrow_forward2. A company is planning to open a maximum of 11 new stores in Chicago. The stores will be built in one of three sizes: a convenience store (open 24 hrs.), a standard store, and an expanded service store. The convivence store requires $4.1215 million to build and 30 employees to operate. The standard store requires $8.25 million to build and 15 employees to operate. The expanded-services store requires $12.375 million to build and 45 employees to operate. The company can dedicate up to $82.5 million for construction, and 300 employees to staff the stores. On average, the convenience store nets $1.2 million annually, the standard store nets $2 million and the expanded service store nets $2.6 million annually. How many of each store should the company build to maximize revenue? Use excel solver.arrow_forward
- An automobile company produces cars in Los Angeles and Detroit and has a warehouse in Atlanta.The company supplies cars to customers in Houston and Tampa. The costs of shipping a car betweenvarious points are listed in the table below, where a blank means that a shipment is not allowed. LosAngeles can produce up to 1100 cars, and Detroit can produce up to 2900 cars. Houston must receive2400 cars, and Tampa must receive 1500 cars. (Include your formulations to receive credit. Thinkcarefully about the transhipment locations.) (a) Determine how to minimize the cost of meeting demands in Houston and Tampa. (b) Modify the answer to part (a) if shipments between Los Angeles and Detroit are not allowed. (c) Modify the answer to part (a) if shipments between Houston and Tampa are allowed at a cost of$5 per car.arrow_forwardUrban Community College is planning to offer courses in Finite Math, Applied Calculus, and Computer Methods. Each section of Finite Math has 40 students and earns the college $40,000 in revenue. Each section of Applied Calculus has 40 students and earns the college $60,000, while each section of Computer Methods has 10 students and earns the college $28,000. Assuming the college wishes to offer a total of seven sections, accommodate 220 students, and bring in $296,000 in revenues, how many sections of each course should it offer?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman