
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Maps
omework i
News
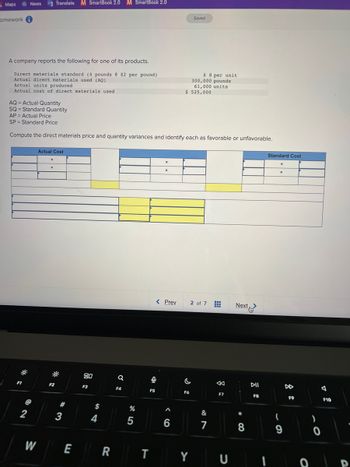
A company reports the following for one of its products.
Direct materials standard (4 pounds @ $2 per pound)
Actual direct materials used (AQ)
Actual units produced
Actual cost of direct materials used
AQ = Actual Quantity
SQ = Standard Quantity
F1
2
Translate M SmartBook 2.0 M SmartBook 2.0
W
AP Actual Price
SP Standard Price
Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances and identify each as favorable or unfavorable.
Actual Cost
X
X
F2
#
3
E
80
F3
$
4
R
a
F4
%
5
F5
T
0
X
X
< Prev
Muslimin
‹6
A
$ 525,000
Saved
$ 8 per unit
300,000 pounds
61,000 units
F6
C
2 of 7
Y
&
7
www
K
F7
U
Next
*
8
DII
F8
Standard Cost
X
X
(
9
DD
F9
0
)
A
F10
D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Vitex, Incorporated manufactures a popular consumer product and it has provided the following data excerpts from its standard cost system: Inputs (1) Standard Quantity or Hours (2) Standard Price or Rate Standard Cost (1) × (2) Direct materials 2.20 pounds $ 16.30 per pound $ 35.86 Direct labor 1.00 hours $ 15.80 per hour $ 15.80 Variable manufacturing overhead 1.00 hours $ 9.50 per hour $ 9.50 Total standard cost per unit $ 61.16 Total Variances Reported Standard Cost* Price or Rate Quantity or Efficiency Direct materials $ 681,340 $ 12,702 F $ 32,600 U Direct labor $ 300,200 $ 4,000 U $ 15,800 U Variable manufacturing overhead $ 180,500 $ 4,100 F $ ?† U *Applied to Work in Process during the period. The company's manufacturing overhead cost is applied to production on the basis of direct labor-hours. All of the materials purchased during the period were used in production. Work in process inventories are insignificant and can be…arrow_forwardDirect material $0.10, Direct laber is $0.25, Variable Overhead is $0.10, Fixed overhead is $0.40 what is the fixed costs per unit, the total cost per unit, and gross margin if 1,600,000 units were produced?arrow_forwardBenoit Company produces three products-A, B, and C. Data concerning the three products follow (per unit): Product A $ 80.00 $ 62.00 $ 81.00 Selling price Variable expenses: Direct materials 24.00 18.00 9.00 Other variable expenses Total variable expenses 24.00 25.40 43.65 48.00 43.40 52.65 Contribution margin $ 32.00 $ 18.60 $ 28.35 Contribution margin ratio 40% 30% 35% The company estimates that it can sell 800 units of each product per month. The same raw material is used in each product. The material costs $3 per pound with a maximum of 5,000 pounds available each month. Required: 1. Calculate the contribution margin per pound of the constraining resource for each product. 2. Which orders would you advise the company to accept first, those for A, B, or C? Which orders second? Third? 3. What is the maximum contribution margin that the company can earn per month if it makes optimal use of its 5,000 pounds of materials? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.…arrow_forward
- PRESENT YOUR ANSWER AS: 10 FAVORABLE OR 10 UNFAVORABLE. The standard product mix for making 12,500 tubes of liquid solder is: Cost /unit Tolal cost 90.00 Kgs. Material A 1,500.00 0.06 Material B 625.00 0.40 250.00 Material C 1,000.00 0.25 250.00 During April, 77,500 tubes were produced from an input of: Kgs. Cost /unit Total cost Material A 8,750.00 0.056 490.00 0. 380 1,425.00 0. 280 1,750.00 Material B 3,750.00 Material C 6,250.00 Compute for the materials yield variance. Indicate whether favorable or unfavorable.arrow_forwardAssume that a company wants to separate a mixed cost into its variable and fixed elements for cost estimation purposes. It provided the following information: Week Units Produced Mixed Cost 1 12,000 $ 35, 300 2 13, 500 $ 39, 500 3 14, 000 $ 41, 100 4 13, 700 $ 39, 620 5 11,500 $ 34,400 6 10, 100 $ 32, 050 7 10,800 $ 32, 380 8 14, 400 $ 41,890 9 11, 200 $ 34, 200 10 13, 200 $ 39, 150 Using least - squares regression, the estimate for the fixed cost per week is closest to:arrow_forwardHw.44.arrow_forward
- Material Material Actual Standard Actual Standard Price Usage Total Supplier Price Price Quantity Quantity Var Var Variance Current $7.50 $7.50 25,000 24,240 $0 Alternative #1 $7.35 $7.50 25,500 24,240 $0 Alternative #2 $7.58 $7.50 24,400 24,240 $0 Standard Quantity is 2.02 components Quantity produced is 12,000 You are a plant manager and have been approached by your purchasing manager about swapping out one of your suppliers. The manager has identified a vendor who will supply a key component at a 2% discount to your current supplier. At the same time, the supervisor of the group approaches you to indicate that the current supplier is not consistently meeting tolerances. The supervisor suggests a second vendor who promises better quality. You decide to run three batches, each with a different component. Results are in the table above. Task 1 Calculate the Material Price Variance for each component. Task 2 Calculate the Material Usage Variance for each component. Task 3 Based on the…arrow_forward1. The standard and actual prices per pound of raw material are $4.00 and $4.50, respectively. A total of 10,500 pounds of raw material was purchased and then used to produce 5,000 units. The quantity standard allows two pounds of the raw material per unit produced. What was the materials quantity variance? a. $5,000 unfavorable b. $5,000 favorable c. $2,000 favorable d. $2,000 unfavorable 2. Referring to the facts in question 1 above, what was the material price variance? a. $5,250 favorable b. $5,250 unfavorable c. $5,000 unfavorable d. $5,000 favorablearrow_forwardEvaluating Selected Cost Driver Assume that a manufacturer of specialized machine parts developed the following total cost estimating equation for manufacturing costs. Y = $14,400 + $1,250 (actual units) a. What is total estimated manufacturing costs if 180 units are produced? $Answer 0arrow_forward
- 8. Given the following data, calculate product cost per unit under variable costing. Direct labor $7 per unit Direct materials $1 per unit Overhead Total variable overhead $20,000 Total fixed overhead $90,000 Expected units to be produced 40,000 units A. $8 per unit B. $8.50 per unit C. $10.25 per unit D. $10.75 per unit E. $12 per unitarrow_forwardRequirements 1. Calculate the inventoriable cost per unit using each level of capacity to compute fixed manufacturing cost per unit 2. Suppose EBL actually produces 250,000 bulbs. Calculate the production-volume variance using each level of capacity to compute the fixed manufacturing overhead allocation rate. 3. Assume EBL has no beginning inventory If this year's actual sales are 187,500 bulbs, calculate operating income for EBL using each type of capacity to compute fixed manufacturing cost per unit please complete requirment part 1,2,3arrow_forwardJSON-5313 Inc. produces Products X5, Y8, and Z9. The following table provides per unit information relating to the three products: Product Y8 X5 Z9 Selling price $ 72.00 $ 54.00 $ 62.00 Variable expenses: Direct materials 21.60 18.00 9.00 21.60 22.50 34.40 43.20 43.40 Other variable expenses Total variable expenses Contribution margin Contribution margin ratio 40.50 $13.50 $28.80 $18.60 40% 25% 30% JSON-5313 has enough demand to sell 700 units of each product per month. Each product requires the same direct materials in its production. The direct materials cost $3 per pound. The company will at most have 4,800 pounds of the direct materials available every month. What is the maximum contribution margin that JSON-5313 can earn per month using its 4,800 pounds of direct materials optimally? O $ 10,800 O $ 13,020 O $ 23,820 O $ 26,320arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education