
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A community's demand for monthly subscription to a streaming music service is shown by the following table. Assume that there are only two firms serving this market (Firm A and Firm B), each firm offers the same quality of service and music selection, and that each firm’s marginal cost is constant and equal to 0 (zero).
(please refer to table provided)
- If this market were highly competitive instead of a duopoly, the quantity of streaming movie subscriptions purchased each month would be ______
- If the two firms agreed to each supply one half of the quantity a
monopoly would supply, the contract would specify that each firm would supply ____
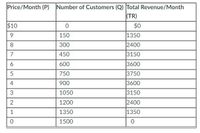
Transcribed Image Text:**Price-Month Analysis Table**
This table represents the relationship between the monthly price (P), the number of customers (Q), and the total revenue per month (TR) for a given service or product. It is a valuable tool for understanding how different pricing strategies can impact customer acquisition and overall revenue.
**Table Breakdown:**
Price/Month (P) | Number of Customers (Q) | Total Revenue/Month (TR)
-----------------|-------------------------|-------------------------
$10 | 0 | $0
$9 | 150 | $1350
$8 | 300 | $2400
$7 | 450 | $3150
$6 | 600 | $3600
$5 | 750 | $3750
$4 | 900 | $3600
$3 | 1050 | $3150
$2 | 1200 | $2400
$1 | 1350 | $1350
$0 | 1500 | $0
**Explanation:**
- **Price/Month (P)**: This column lists the price of the product or service per month, ranging from $10 to $0.
- **Number of Customers (Q)**: This column indicates the number of customers willing to pay the corresponding price in the first column.
- **Total Revenue/Month (TR)**: This column represents the total revenue generated from the number of customers at the given price point. It is calculated by multiplying the price (P) by the number of customers (Q).
**Key Observations:**
1. When the price is at the highest ($10), there are no customers, resulting in zero revenue.
2. As the price decreases from $10 to $5, the number of customers increases, leading to increased total revenue.
3. The maximum total revenue of $3750 is achieved at a price point of $5 with 750 customers.
4. After the peak at $5, even though the number of customers continues to increase with further price decreases, the total revenue starts to decrease again.
5. At the lowest price ($0), there are 1500 customers, but the total revenue returns to zero because the service or product is provided for free.
This table provides critical insights for companies to determine the optimal pricing strategy that maximizes revenue while considering the behavior of their
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Firm 1 and firm 2 are Bertrand duopoloists. Firm 1 has a marginal cost of $6.00 per unit, and firm 2 has a marginal cost of $8.01 per unit. The demand for their product is p=23.00−Q, where Q is the total quantity demanded. How much does each firm sell in equilibrium? Assume that prices can only be set to the nearest cent, firms split the market if they set the same price, and there are no fixed costs. Firm 1 production:______ Firm 2 production:______ What are the profits for each firm in equilibrium? Firm 1 profit: $______ Firm 2 profit: $______arrow_forwardSuppose oil production in the Gulf of Mexico was a symmetric horizontal oligopoly in Cournot competition. Assume there are two producers, each with a constant marginal cost of production of $50 per barrel. Let the demand function for oil in the region be D(p) = 12000 – 20p, where demand is measured in barrels per day. (You will need to calculate inverse demand from demand before moving on). What would the perfectly competitive equilibrium price and quantity be? What would be the consumer surplus and producer surplus? Draw each firm’s residual inverse demand curve. Calculate the Cournot-Nash equilibrium price and quantity. What is the total consumer surplus, total producer surplus across the two firms, and deadweight loss?arrow_forwardConsider two Cournot oligopolists, firm 1 and firm 2, in a homogenous product market. The market demand is P = 100 - 3Q and each firm has a constant marginal cost MC=10. The market price of equilibrium and total quantity in the market is: Select one: a. P* 30 and Q* = 20 O b. P* 40 and Q* = 20 ○ c. P* = 40 and Q* = 30 O d. P*20 and Q* = 30arrow_forward
- PLEASE CHECK THIS HOW TO SOLVE PLEASE TEACH EXPLAIN STEP BY STEParrow_forwardConsider a Cournot duopoly. The market demand function is P = 180 – 2(q₂ + q₂), where P is the market price, q₂ is the output produced by Firm 1 and q₂ is the output produced by Firm 2. The two firms have a constant marginal cost c = 30. What is the total output in this market? Round your answer to the nearest integer (e.g. 50)arrow_forwardConsider a market that is a Bertrand oligopoly with 5 firms in the market. Each of these firms produce an identical product and each have the same cost function of C(Q) = 80Q. The inverse market demand for this product is P = 2480 – 2Q. What is the equilibrium market price?arrow_forward
- See image for questions partsarrow_forwardHelp me pleasearrow_forwardIn the mobile phone market, Samsung and Apple constitute a duopoly in the production of devices.The American firm has the following demand q(a) = 10 - p(a )+ 0.25p(s), and the Korean firm, q(s) = 20 -p(s)+ 0.5p(a). Because both firms assembly their devices in China, their cost structure is the same andequal to ?(q) = 10q, answer the following questions.a) What would be the equilibrium (quantity, price, and profit) in this market, and interpret youranswer.b) If they decide to form a cartel, what are the new quantities, prices, and profits? NB.a=apple and s=Samsungarrow_forward
- Suppose Giocattolo of Italy and American Toy Company of the United States are the only two firms producing toys for sale in the U.S. market. Each firm realizes constant long-term costs so that the average total cost (ATC) equals the marginal cost (MC) at each level of output. Thus, MCo = ATCO is the long-term market supply schedule for toys. Suppose Giocattolo and American Toy Company operate as competitors, and the cost schedules of each company are MCo = ATCO = $10. On the following graph, use the grey point (star symbol) to identify the competitive market equilibrium. Then, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to identify consumer surplus in this case. Note: Select and drag the point from the palette to the graph. Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes. Then select and drag the shaded region from the palette to the graph. To resize the shaded region, select one of the points and move to the desired position. ? PRICE (Dollars per toy) 20 18 16 14 10 00 6 4 2 0…arrow_forwardConsider a duopoly where firms compete in prices and firms do not have any capacity constraints. Market demand is P(Q)=45-4Q, and each firm faces a marginal cost of $9 per unit. How much is each firm's total variable cost if firms equally divide the market at Nash equilibrium?arrow_forwardConsider two Cournot oligopolists, firm 1 and firm 2, in a homogenous product market. The market demand is P = 100 – 3Q and each firm has a constant marginal cost MC=10. The Cournot equilibrium quantity for each firm is: a. 7.5 b. 10 c. 5 d.15arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education